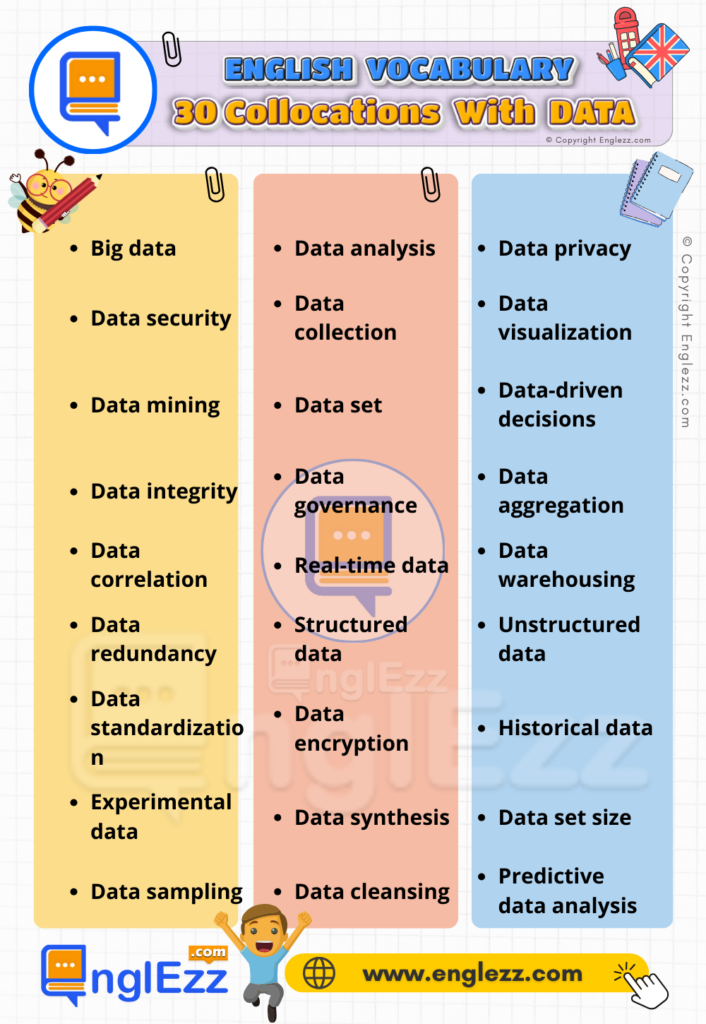
In today’s data-driven world, mastering collocations—common combinations of words used with “data”—can greatly enhance your communication and writing skills. In this blog post, we’ll explore 30 essential collocations with data, providing definitions, phonetic transcriptions, and practical examples to enrich your vocabulary and writing prowess.
Table of Contents
- 30 Collocations with Data 📊 Boost Your Understanding of Key Phrases
- #1. Big Data 🌐
- #2. Data Analysis 🔍
- #3. Data Privacy 🔐
- #4. Data Security 🔒
- #5. Data Visualization 📈
- #6. Data Collection 📋
- #7. Data Mining ⛏️
- #8. Data Set 📚
- #9. Data-driven Decisions 📈
- #10. Data Integrity ✅
- #11. Data Governance 📜
- #12. Data Aggregation 📊
- #13. Data Correlation 🔗
- #14. Real-time Data ⏱️
- #15. Data Warehousing 🏢
- #16. Data Redundancy ♻️
- #17. Structured Data 🗃️
- #18. Unstructured Data 📂
- #19. Data Standardization 📏
- #20. Data Encryption 🔐
- #21. Historical Data 📜
- #22. Experimental Data 🧪
- #23. Data Synthesis 🧩
- #24. Data Set Size 📏
- #25. Data Sampling 📉
- #26. Data Cleansing 🧼
- #27. Predictive Data Analysis 🔮
- #28. Data Integration 🔗
- #29. Data Benchmarking 📈
- #30. Data Forecasting 📊
- Collocations With DATA Table
- Most Common Collocations With DATA Worksheet
- Wrapping Up
30 Collocations with Data 📊 Boost Your Understanding of Key Phrases
Collocations help convey precise meanings and can improve your SEO content by making it more relevant and engaging. For instance, using the right collocations can boost your content’s visibility on search engines, making it easier for users to find and interact with your material. Whether you’re writing educational materials, blog posts, or technical documents, understanding these common phrases will help you create more impactful and clear content.
#1. Big Data 🌐
Definition: Large and complex datasets that are difficult to process using traditional data management tools.
Phonetic Transcription: /bɪɡ ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Big data analytics can reveal hidden patterns in consumer behavior.”
- “Companies are investing heavily in big data technologies to stay competitive.”
#2. Data Analysis 🔍
Definition: The process of examining and interpreting data to extract useful information.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə əˈnæləsɪs/
Examples:
- “Data analysis helps businesses make informed decisions.”
- “The team is currently focused on data analysis to understand the latest trends.”
#3. Data Privacy 🔐
Definition: The protection of personal information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈpraɪvəsi/
Examples:
- “Data privacy is a major concern for users of online services.”
- “Ensuring data privacy is essential for maintaining user trust.”
#4. Data Security 🔒
Definition: Measures and protocols designed to protect data from breaches or attacks.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə sɪˈkjʊərəti/
Examples:
- “Data security protocols must be updated regularly to defend against new threats.”
- “Organizations are investing in advanced data security systems to safeguard sensitive information.”
#5. Data Visualization 📈
Definition: The graphical representation of data to help users understand complex information.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˌvɪzjʊəlaɪˈzeɪʃən/
Examples:
- “Effective data visualization can turn raw numbers into actionable insights.”
- “The report includes several data visualization tools to enhance understanding.”
#6. Data Collection 📋
Definition: The process of gathering and measuring information to analyze and use.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə kəˈlɛkʃən/
Examples:
- Data collection methods vary depending on the research objectives.”
- “Accurate data collection is crucial for reliable results.”
#7. Data Mining ⛏️
Definition: The practice of analyzing large datasets to discover patterns and relationships.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈmaɪnɪŋ/
Examples:
- “Data mining techniques are used to uncover trends in consumer purchasing behavior.”
- “The company employs data mining to improve its marketing strategies.”
#8. Data Set 📚
Definition: A collection of related data points or records that are analyzed together.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə sɛt/
Examples:
- “The researchers analyzed a data set comprising millions of health records.”
- “Each data set should be properly labeled for accurate analysis.”
#9. Data-driven Decisions 📈
Definition: Choices and strategies based on data analysis rather than intuition alone.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈdrɪvən dɪˈsɪʒənz/
Examples:
- “Data-driven decisions help organizations optimize their operations.”
- “Adopting a data-driven approach can lead to more effective marketing campaigns.”
#10. Data Integrity ✅
Definition: The accuracy and consistency of data over its lifecycle.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ɪnˈtɛɡrɪti/
Examples:
- “Maintaining data integrity is critical for reliable reporting.”
- “The system ensures data integrity through regular backups and validation checks.”
#11. Data Governance 📜
Definition: The framework for managing and ensuring the quality and security of data.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈɡʌvərnəns/
Examples:
- “Effective data governance policies are essential for compliance with regulations.”
- “Data governance helps streamline data management practices across departments.”
#12. Data Aggregation 📊
Definition: The process of combining data from different sources to create a comprehensive dataset.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˌæɡrɪˈɡeɪʃən/
Examples:
- “Data aggregation allows for a holistic view of market trends.”
- “The system supports data aggregation from multiple databases.”
#13. Data Correlation 🔗
Definition: The relationship between two or more variables in a dataset.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˌkɔːrəˈleɪʃən/
Examples:
- “Data correlation analysis can help identify factors influencing sales performance.”
- “The study found a strong correlation between temperature and energy consumption.”
#14. Real-time Data ⏱️
Definition: Information that is available immediately as it is generated.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈriːəl taɪm ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Real-time data monitoring is crucial for effective decision-making in finance.”
- “The application provides real-time data updates for traffic conditions.”
#15. Data Warehousing 🏢
Definition: The process of storing large volumes of data in a central repository for analysis.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈwɛəraʊsɪŋ/
Examples:
- “Data warehousing enables comprehensive reporting and analysis.”
- “The company invested in data warehousing to consolidate its information.”
#16. Data Redundancy ♻️
Definition: The unnecessary repetition of data within a database or system.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə rɪˈdʌndənsi/
Examples:
- “Data redundancy can lead to increased storage costs and reduced efficiency.”
- “The system is designed to minimize data redundancy and improve performance.”
#17. Structured Data 🗃️
Definition: Data organized in a predefined format, making it easy to analyze and query.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈstrʌktʃərd ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Structured data is typically stored in databases and spreadsheets.”
- “The website uses structured data to enhance search engine visibility.”
#18. Unstructured Data 📂
Definition: Data that lacks a predefined format, such as text, images, or social media posts.
Phonetic Transcription: /ʌnˈstrʌktʃərd ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Unstructured data requires specialized tools for effective analysis.”
- “The company uses natural language processing to handle unstructured data.”
#19. Data Standardization 📏
Definition: The process of converting data into a consistent format for easier analysis and comparison.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˌstændərdaɪˈzeɪʃən/
Examples:
- “Data standardization helps ensure consistency across different systems.”
- “The project includes a phase for data standardization to improve data quality.”
#20. Data Encryption 🔐
Definition: The method of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ɪnˈkrɪpʃən/
Examples:
- “Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information in transit.”
- “The software employs advanced data encryption techniques to secure user data.”
#21. Historical Data 📜
Definition: Data collected over a period of time, used for trend analysis and forecasting.
Phonetic Transcription: /hɪsˈtɒrɪkəl ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Historical data provides valuable insights for long-term planning.”
- The report analyzed historical data to predict future market trends.
#22. Experimental Data 🧪
Definition: Data obtained through scientific experiments and research.
Phonetic Transcription: /ɪkˌspɛrɪˈmɛntəl ˈdeɪtə/
Examples:
- “Experimental data is crucial for validating scientific hypotheses.”
- “The research team collected experimental data to test the new drug.”
#23. Data Synthesis 🧩
Definition: Combining data from various sources to form a comprehensive overview.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈsɪnθəsɪs/
Examples:
- “Data synthesis is used to integrate findings from multiple studies.”
- “The analysis involved data synthesis to create a unified report.”
#24. Data Set Size 📏
Definition: The amount of data included in a dataset.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə sɛt saɪz/
Examples:
- “The data set size can impact the performance of data processing tools.”
- “Large data set sizes require more computational resources for analysis.”
#25. Data Sampling 📉
Definition: The process of selecting a subset of data from a larger dataset for analysis.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈsæmplɪŋ/
Examples:
- “Data sampling helps reduce the computational load during analysis.”
- “The study used data sampling to estimate population trends.”
#26. Data Cleansing 🧼
Definition: The process of identifying and correcting errors or inconsistencies in data.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈklɛnzɪŋ/
Examples:
- “Data cleansing is essential for ensuring the accuracy of analysis results.”
- “The data cleansing process involved removing duplicate records and correcting errors.”
#27. Predictive Data Analysis 🔮
Definition: Using historical data to predict future trends and behaviors.
Phonetic Transcription: /prɪˈdɪktɪv ˈdeɪtə əˈnæləsɪs/
Examples:
- “Predictive data analysis can forecast customer purchasing patterns.”
- “The company uses predictive data analysis to anticipate market shifts.”
#28. Data Integration 🔗
Definition: Combining data from different sources to provide a unified view.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˌɪntɪˈɡreɪʃən/
Examples:
- “Data integration helps create a comprehensive overview of organizational performance.”
- “The platform supports data integration from various external sources.”
#29. Data Benchmarking 📈
Definition: Comparing data against standards or best practices to assess performance.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈbɛnʃmɑːrkɪŋ/
Examples:
- Data benchmarking is used to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing strategies.”
- “The report included data benchmarking to measure progress against industry standards.”
#30. Data Forecasting 📊
Definition: Using historical data to make predictions about future events.
Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdeɪtə ˈfɔːrkæstɪŋ/
Examples:
- “Data forecasting helps businesses plan for future demand and resource allocation.”
- “The tool provides data forecasting capabilities to support strategic decision-making.”
Collocations With DATA Table
| Big data | Data analysis | Data privacy |
| Data security | Data collection | Data visualization |
| Data mining | Data set | Data-driven decisions |
| Data integrity | Data governance | Data aggregation |
| Data correlation | Real-time data | Data warehousing |
| Data redundancy | Structured data | Unstructured data |
| Data standardization | Data encryption | Historical data |
| Experimental data | Data synthesis | Data set size |
| Data sampling | Data cleansing | Predictive data analysis |
This table includes a variety of common collocations related to “data” to help you enhance your content or study vocabulary.
Most Common Collocations With DATA Worksheet

Wrapping Up
Understanding and effectively using collocations with “data” can significantly enhance your writing and communication skills. These common phrases help convey precise meanings and can make your content more engaging and easier to understand.
By incorporating these collocations into your educational materials, blog posts, or any other written content, you not only improve clarity but also boost your content’s SEO performance. Mastering these collocations enables you to produce well-rounded and professional content that resonates with your audience.
As you continue to explore and utilize these phrases, you’ll find that your ability to articulate complex data-related concepts becomes much more refined. This, in turn, will help you achieve your content goals and stand out in a competitive digital landscape.
Happy learning! 😊







👍📚 Unlock the full potential of your data-related writing with our latest post on collocations! 🌟 Dive into essential phrases and boost your content skills effortlessly. and don’t forget to follow and like EnglEzz for more valuable tips! Check it out here:
.
https://www.englezz.com/30-collocations-with-data/
#englezz #DataScience #ContentWriting #SEO #EducationalMaterials #BigData #WritingTips
Wow superb blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is magnificent as well as the content