Public speaking is an invaluable skill that plays a crucial role in both personal and professional settings. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, speaking at a conference, or addressing a community group, understanding the key terms associated with public speaking can significantly enhance your effectiveness and confidence. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the 50 most common public speaking English terms, providing clear definitions, phonetic transcriptions, and practical examples to illustrate each concept.
50 Public Speaking English Terms Every Student Must Know
Mastering these terms not only helps you communicate your ideas more clearly but also enables you to engage and persuade your audience effectively.
Whether you’re a novice looking to build a solid foundation or an experienced speaker aiming to refine your skills, this resource is designed to support your journey. By familiarizing yourself with these essential terms, you’ll be better equipped to craft compelling speeches, deliver them with impact, and connect with your audience on a deeper level.
From understanding the nuances of body language to mastering the art of rhetoric, each term is broken down to ensure you grasp its significance and application. Let’s embark on this journey to elevate your public speaking prowess and unlock new opportunities for success.
#1. Audience 👥
Definition: The group of people who listen to a speaker during a presentation or speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈɔː.di.əns/ Examples:
- Before preparing your speech, it’s essential to understand your audience’s interests and expectations.
- Engaging the audience with questions can make your presentation more interactive and memorable.
#2. Body Language 🤸
Definition: Nonverbal communication through gestures, posture, and facial expressions. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈbɒd.i ˈlæŋ.ɡwɪdʒ/ Examples:
- Effective body language, such as maintaining eye contact, can enhance your credibility as a speaker.
- Avoiding closed body language, like crossing your arms, helps in creating a more approachable presence.
#3. Call to Action 📢
Definition: A statement designed to prompt an immediate response or encourage a specific action from the audience. Phonetic Transcription: /kɔːl tuː ˈæk.ʃən/ Examples:
- At the end of her speech, she included a call to action, urging the audience to volunteer for the community project.
- A strong call to action can significantly increase audience engagement and participation.
#4. Closure 🔚
Definition: The concluding part of a speech where the speaker summarizes key points and leaves a lasting impression. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈkləʊ.ʒər/ Examples:
- A powerful closure can reinforce your message and leave the audience with something to remember.
- He used a compelling story in the closure to highlight the importance of his main argument.
#5. Content 📄
Definition: The information, ideas, and messages conveyed in a speech or presentation. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈkɒn.tɛnt/ Examples:
- The content of your speech should be well-researched and relevant to your audience’s interests.
- Clear and organized content helps in maintaining the audience’s attention throughout the presentation.
#6. Delivery 🎤
Definition: The manner in which a speaker presents their speech, including voice modulation, pacing, and emphasis. Phonetic Transcription: /dɪˈlɪv.ər.i/ Examples:
- Her confident delivery made the complex topic easy to understand for the audience.
- Practicing your delivery can help you speak more smoothly and reduce nervousness.
#7. Ethos 🏛️
Definition: A rhetorical appeal that establishes the speaker’s credibility and trustworthiness. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈiː.θɒs/ Examples:
- By sharing her extensive experience, she built strong ethos with the audience.
- Establishing ethos early in your speech can make your arguments more persuasive.
#8. Feedback 🔄
Definition: Responses or reactions from the audience that provide insight into the effectiveness of the speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈfiːd.bæk/ Examples:
- Constructive feedback from your peers can help you improve your public speaking skills.
- Paying attention to audience feedback during your speech allows you to adjust your delivery in real-time.
#9. Gestures 🤲
Definition: Movements of the hands, arms, or other parts of the body to emphasize points or convey messages. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈdʒɛs.tʃərz/ Examples:
- Using gestures while speaking can make your presentation more dynamic and engaging.
- Overusing gestures can be distracting, so it’s important to use them purposefully.
#10. Hook 🎣
Definition: An attention-grabbing opening statement or question designed to engage the audience from the start. Phonetic Transcription: /hʊk/ Examples:
- She began her speech with a startling statistic as a hook to capture the audience’s interest.
- A well-crafted hook can set the tone for the rest of your presentation.
#11. Impromptu 🎙️
Definition: A speech given without prior preparation or notes. Phonetic Transcription: /ɪmˈprɒm.ptuː/ Examples:
- He excelled at impromptu speaking, often delivering clear and coherent thoughts on the spot.
- Practicing impromptu speeches can enhance your ability to think quickly during presentations.
#12. Introduction 🗣️
Definition: The beginning section of a speech where the speaker introduces themselves and outlines the main points. Phonetic Transcription: /ˌɪn.trə.dʌkˈʃən/ Examples:
- A strong introduction sets the stage for the rest of your speech and captures the audience’s attention.
- She used a personal anecdote in her introduction to connect with the audience emotionally.
#13. Keynote 🗝️
Definition: The main or central theme of a speech or presentation, often delivered by a prominent speaker. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈkiː.nəʊt/ Examples:
- The keynote address at the conference highlighted the importance of innovation in technology.
- Crafting a clear keynote helps in maintaining focus and coherence throughout your speech.
#14. Language 🗨️
Definition: The choice of words and style of expression used in a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈlæŋ.ɡwɪdʒ/ Examples:
- Using simple and clear language ensures that your message is easily understood by the audience.
- Adapting your language to suit your audience can make your speech more relatable and effective.
#15. Main Idea 💡
Definition: The central concept or primary message that a speaker wants to convey. Phonetic Transcription: /meɪn aɪˈdiː.ə/ Examples:
- Identifying your main idea helps in structuring your speech logically.
- Each supporting point in your presentation should reinforce the main idea.
#16. Metaphor 🌀
Definition: A figure of speech that makes a comparison between two unrelated things by stating one is the other. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈmɛt.ə.fɔːr/ Examples:
- She used a metaphor, saying “time is a thief,” to illustrate the fleeting nature of life.
- Metaphors can make complex ideas more relatable and easier to understand for the audience.
#17. Narration 📖
Definition: The act of telling a story or recounting events as part of a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /nəˈreɪ.ʃən/ Examples:
- Incorporating narration in your speech can help illustrate your points more vividly.
- His effective narration of personal experiences made the presentation more engaging.
#18. Nonverbal Communication 👐
Definition: The transmission of messages without using words, including body language, facial expressions, and gestures. Phonetic Transcription: /nɒnˈvɜː.bəl kəˌmjuː.nɪˈkeɪ.ʃən/ Examples:
- Nonverbal communication, such as nodding, can signal agreement and understanding to your audience.
- Being aware of your nonverbal cues helps in conveying confidence and sincerity.
#19. Opener 🚪
Definition: The initial part of a speech designed to capture the audience’s attention and introduce the topic. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈəʊ.pənər/ Examples:
- Starting with a surprising fact served as an effective opener for her presentation.
- A compelling opener can set a positive tone for the rest of your speech.
#20. Outline 📝
Definition: A structured plan that organizes the main points and supporting details of a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈaʊt.laɪn/ Examples:
- Creating an outline before writing your speech helps in organizing your thoughts logically.
- An outline ensures that you cover all necessary points without deviating from your main topic.
#21. Persuasion 🗣️➡️🧠
Definition: The act of convincing the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take specific actions. Phonetic Transcription: /pəˌsweəˈʃən/ Examples:
- Effective persuasion techniques can increase the likelihood of your audience supporting your ideas.
- Using emotional appeals is a common strategy in persuasion to connect with the audience on a deeper level.
#22. Pitch 📈
Definition: A short, persuasive speech aimed at selling an idea, product, or oneself. Phonetic Transcription: /pɪtʃ/ Examples:
- She delivered a compelling pitch to potential investors, securing the necessary funding for her startup.
- Practicing your pitch can help you communicate your ideas more clearly and confidently.
#23. Practice 🏋️♂️
Definition: Repeated rehearsal of a speech to improve delivery and reduce anxiety. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈpræk.tɪs/ Examples:
- Regular practice can enhance your confidence and smoothness during actual presentations.
- Recording your practice sessions allows you to identify areas for improvement.
#24. Proxemics 📏
Definition: The study of personal space and how distance affects communication. Phonetic Transcription: /prɒkˈsiː.mɪks/ Examples:
- Understanding proxemics helps in maintaining appropriate distance from the audience, making them feel comfortable.
- Adjusting your proximity to the audience can influence their perception of your confidence and authority.
#25. Public Speaking Anxiety 😰
Definition: The fear or nervousness associated with speaking in front of an audience. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈpʌb.lɪk ˈspiː.kɪŋ æŋˈzaɪ.ə.ti/ Examples:
- Techniques like deep breathing and visualization can help manage public speaking anxiety.
- Overcoming public speaking anxiety is essential for delivering effective and confident presentations.
#26. Rhetoric 🗣️✨
Definition: The art of effective or persuasive speaking, often employing figures of speech and other compositional techniques. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈrɛt.ər.ɪk/ Examples:
- Mastering rhetoric allows speakers to influence and inspire their audiences more effectively.
- She used rhetoric to highlight the importance of environmental conservation during her speech.
#27. Rehearsal 🎭
Definition: The process of practicing a speech multiple times before the actual presentation. Phonetic Transcription: /rɪˈhɜː.səl/ Examples:
- Conducting a rehearsal helps in identifying and correcting any flaws in your speech delivery.
- Group rehearsals can provide valuable feedback and enhance your performance.
#28. Repetition 🔁
Definition: The intentional reuse of words or phrases to emphasize a point or make it more memorable. Phonetic Transcription: /ˌrɛp.ɪˈtɪʃ.ən/ Examples:
- Repetition of key phrases can reinforce your main ideas and ensure they stick with the audience.
- Overusing repetition may make your speech monotonous, so it’s important to use it sparingly.
#29. Resolution 🏁
Definition: A firm decision to do or not do something, often concluded at the end of a speech to inspire action. Phonetic Transcription: /ˌrɛz.əˈluː.ʃən/ Examples:
- He ended his speech with a resolution to work towards a more sustainable future.
- A strong resolution can motivate the audience to take the desired action.
#30. Rhythm 🥁
Definition: The pattern of sounds and the flow of speech, including pacing and timing. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈrɪð.əm/ Examples:
- Maintaining a steady rhythm helps in keeping the audience engaged and attentive.
- Varying your rhythm can add emphasis and prevent your speech from becoming monotonous.
#31. Rhetorical Questions ❓
Definition: Questions posed to the audience without expecting an actual response, used to provoke thought or emphasize a point. Phonetic Transcription: /rɪˈtər.ɪ.kəl ˈkwɛs.tʃənz/ Examples:
- “What would you do if you had unlimited resources?” is a rhetorical question that encourages the audience to think deeply.
- Using rhetorical questions can effectively engage the audience and highlight key points.
#32. Signpost 🪧
Definition: Verbal cues that guide the audience through the structure of a speech, indicating transitions and key points. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈsaɪn.pəʊst/ Examples:
- Phrases like “firstly,” “in addition,” and “finally” serve as signposts to help the audience follow your speech.
- Effective use of signposts ensures that your speech is organized and easy to understand.
#33. Slideshow 📽️
Definition: A visual presentation consisting of a series of images or slides used to support and enhance a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈslaɪd.ʃəʊ/ Examples:
- Incorporating a slideshow can help illustrate complex data and keep the audience engaged.
- Ensure that your slideshow complements your speech without distracting from your message.
#34. Stage Presence 🎭
Definition: The ability to project confidence, charisma, and authority while speaking on stage. Phonetic Transcription: /steɪdʒ ˈprɛz.əns/ Examples:
- Strong stage presence can captivate the audience and make your speech more impactful.
- Practicing your posture and movement can enhance your stage presence during presentations.
#35. Storytelling 📚
Definition: The use of stories or anecdotes to illustrate points and engage the audience emotionally. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈstɔːr.iˌtɛl.ɪŋ/ Examples:
- Effective storytelling can make your speech more relatable and memorable for the audience.
- She used personal stories to highlight the challenges and successes of her project.
#36. Speech 🗣️
Definition: A formal address or discourse delivered to an audience. Phonetic Transcription: /spiːtʃ/ Examples:
- Preparing a well-structured speech is key to delivering your message effectively.
- His inspiring speech motivated the team to strive for excellence.
#37. Supporting Evidence 📊
Definition: Data, facts, examples, or quotations used to back up and strengthen the main points of a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /səˈpɔː.tɪŋ ˈɛv.ɪ.dəns/ Examples:
- Providing supporting evidence can make your arguments more credible and convincing.
- She included statistical data as supporting evidence to reinforce her claims.
#38. Tone 🎶
Definition: The speaker’s attitude or emotional quality conveyed through their voice and choice of words. Phonetic Transcription: /təʊn/ Examples:
- A positive tone can inspire and uplift your audience during a motivational speech.
- Maintaining a consistent tone helps in delivering a clear and coherent message.
#39. Transition 🔀
Definition: The process of moving smoothly from one point or section of a speech to another. Phonetic Transcription: /trænˈzɪʃən/ Examples:
- Effective transitions ensure that your speech flows logically and keeps the audience engaged.
- Using transitional phrases like “moving on to” can help guide the audience through your presentation.
#40. Visual Aids 🖼️
Definition: Tools such as images, charts, graphs, and videos used to enhance and clarify the content of a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈvɪʒ.u.əl eɪdz/ Examples:
- Incorporating visual aids can help illustrate complex concepts and keep the audience interested.
- Ensure that your visual aids are clear, relevant, and support your main points effectively.
#41. Vocal Variety 🎤🎶
Definition: The variation in pitch, pace, volume, and tone of the speaker’s voice to maintain interest and emphasize points. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈvəʊ.kəl vəˈraɪ.ə.ti/ Examples:
- Using vocal variety can make your speech more dynamic and prevent it from sounding monotonous.
- Emphasizing key words with a higher pitch can highlight important aspects of your message.
#42. Warm-up 🔥
Definition: Exercises or activities performed before speaking to prepare the voice and reduce nervousness. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈwɔːm.ʌp/ Examples:
- Performing vocal warm-up exercises can improve your clarity and projection during a speech.
- A short mental warm-up can help calm your nerves and enhance your focus before presenting.
#43. Audience Analysis 🕵️♂️
Definition: The process of understanding the demographics, interests, and needs of the audience to tailor the speech accordingly. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈɔː.di.əns əˈnæl.ɪ.sɪs/ Examples:
- Conducting an audience analysis helps in crafting a message that resonates with your listeners.
- She adjusted her language and examples based on the audience analysis to better connect with the attendees.
#44. Benchmarking 📏📈
Definition: Comparing your speaking performance against established standards or examples to identify areas for improvement. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈbɛn.tʃmɑː.kɪŋ/ Examples:
- Benchmarking against skilled speakers can provide valuable insights into enhancing your own public speaking skills.
- Regular benchmarking helps in tracking your progress and setting achievable goals for improvement.
#45. Bullet Points ••
Definition: Short, concise statements used to outline key information or main ideas in a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈbʊl.ɪt pɔɪnts/ Examples:
- Using bullet points in your notes can help you stay organized and ensure you cover all essential topics.
- Bullet points on slides can provide a clear structure and highlight the main points of your presentation.
#46. Clarity 🔍
Definition: The quality of being clear and easy to understand in speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈklær.ɪ.ti/ Examples:
- Speaking with clarity ensures that your audience comprehends your message without confusion.
- Avoiding jargon and using simple language can enhance the clarity of your speech.
#47. Contingency 🛠️
Definition: Plans or strategies in place to address unexpected issues or challenges during a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /kənˈtɪn.dʒən.si/ Examples:
- Having a contingency plan for technical difficulties can help maintain your composure during a presentation.
- Preparing for potential questions is a contingency strategy to ensure you handle the Q&A session smoothly.
#48. Debate ⚖️
Definition: A formal discussion on a particular topic where opposing arguments are presented. Phonetic Transcription: /dɪˈbeɪt/ Examples:
- Participating in a debate can sharpen your public speaking and critical thinking skills.
- She structured her speech like a debate, presenting both sides before advocating for her position.
#49. Emphasis 🎯
Definition: The special importance or significance placed on certain words or ideas in a speech. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈɛmf.ə.sɪs/ Examples:
- Using emphasis on key points can make them stand out and be more memorable for the audience.
- He varied his tone to add emphasis, highlighting the most critical aspects of his message.
#50. Feedback Loop 🔁📬
Definition: The ongoing process of receiving and incorporating feedback to continuously improve public speaking skills. Phonetic Transcription: /ˈfiːd.bæk luːp/ Examples:
- Establishing a feedback loop with peers can provide constructive insights to enhance your future presentations.
- An effective feedback loop allows you to refine your speaking techniques based on audience reactions and critiques.
Incorporating these terms into your public speaking repertoire not only enhances your ability to communicate but also builds your credibility as a speaker. Whether it’s leveraging body language to convey confidence, using rhetorical devices to persuade, or employing visual aids to clarify complex ideas, each element contributes to a more impactful and memorable presentation.
Additionally, understanding concepts like audience analysis and contingency planning ensures that you are prepared to address the diverse needs and potential challenges that may arise during your speech.
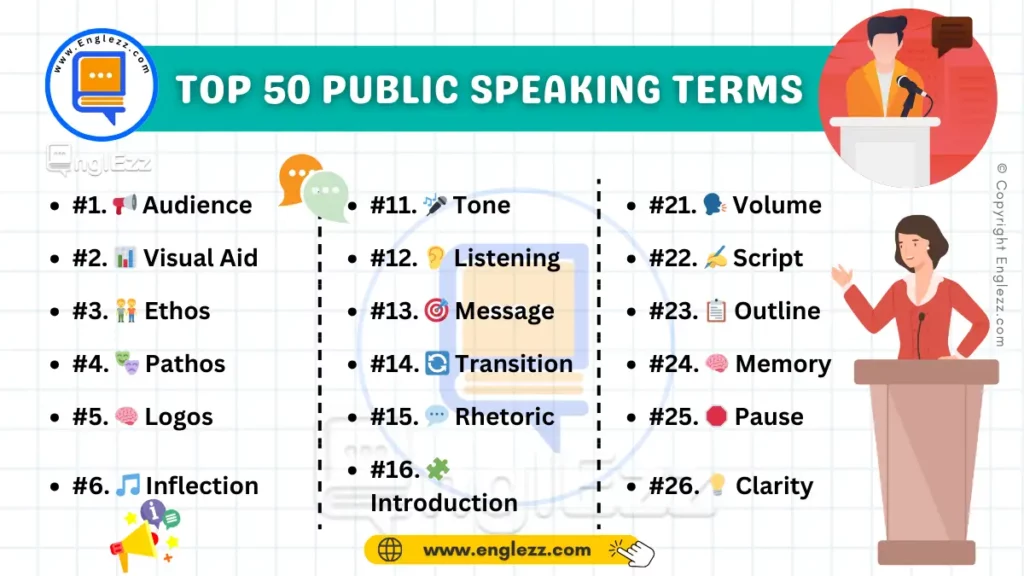
Common Public Speaking English Terms Table
| #1. 📢 Audience | #11. 🎤 Tone | #21. 🗣️ Volume |
| #2. 📊 Visual Aid | #12. 👂 Listening | #22. ✍️ Script |
| #3. 🧑🤝🧑 Ethos | #13. 🎯 Message | #23. 📋 Outline |
| #4. 🎭 Pathos | #14. 🔄 Transition | #24. 🧠 Memory |
| #5. 🧠 Logos | #15. 💬 Rhetoric | #25. 🛑 Pause |
| #6. 🎵 Inflection | #16. 🧩 Introduction | #26. 💡 Clarity |
| #7. 🕵️♂️ Enunciation | #17. 🕰️ Timing | #27. 🎤 Microphone |
| #8. 🚶♂️ Gestures | #18. 🌐 Eye Contact | #28. 📅 Preparation |
| #9. 🧘♂️ Poise | #19. 👁️ Visual Cues | #29. 🎭 Rehearsal |
| #10. 🌟 Confidence | #20. 🎭 Expression | #30. 📝 Feedback |
Conclusion
Mastering public speaking is a journey that involves understanding and effectively utilizing various terms and concepts. By familiarizing yourself with these 50 common public speaking English terms, you equip yourself with the tools necessary to craft compelling speeches, engage your audience, and deliver your message with confidence and clarity. Each term, from “Audience” to “Feedback Loop,” plays a pivotal role in the overall effectiveness of your presentation, influencing how your message is received and remembered.
As you continue to develop your public speaking skills, remember that practice and continual learning are key. Use the definitions and examples provided as a foundation, and strive to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. Seek feedback, engage in rehearsals, and remain adaptable to refine your techniques further.
Public speaking is not just about delivering information; it’s about connecting with your audience, inspiring action, and leaving a lasting impression. Embrace these terms, integrate them into your speaking strategy, and watch your confidence and effectiveness soar to new heights.
By dedicating time to understand and implement these fundamental public speaking terms, you set yourself on a path to becoming a more persuasive, engaging, and successful communicator. Whether you’re speaking in a boardroom, on stage, or in a virtual setting, these principles will guide you in delivering speeches that resonate and make a meaningful impact.








🌟 Elevate your public speaking game! Discover essential terms that will refine your skills and impress your audience. Don’t miss out—follow and like @EnglEzz for more insights! 🌟
.
https://www.englezz.com/common-public-speaking-english-terms/
.
#EnglEzz #vocabulary #linguistics #learnenglish #publicspeaking #communication #oratory #speech #presentation #softskills