American civilization is a rich tapestry of history, culture, and societal norms that have shaped the United States into the nation it is today. Understanding the key terms and concepts that define this civilization is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the essence of American life, politics, and social structures. Whether you’re a student of history, a curious traveler, or simply someone interested in expanding your knowledge of American culture, this comprehensive guide to the 50 most common American civilization terms will serve as an invaluable resource.
Table of Contents
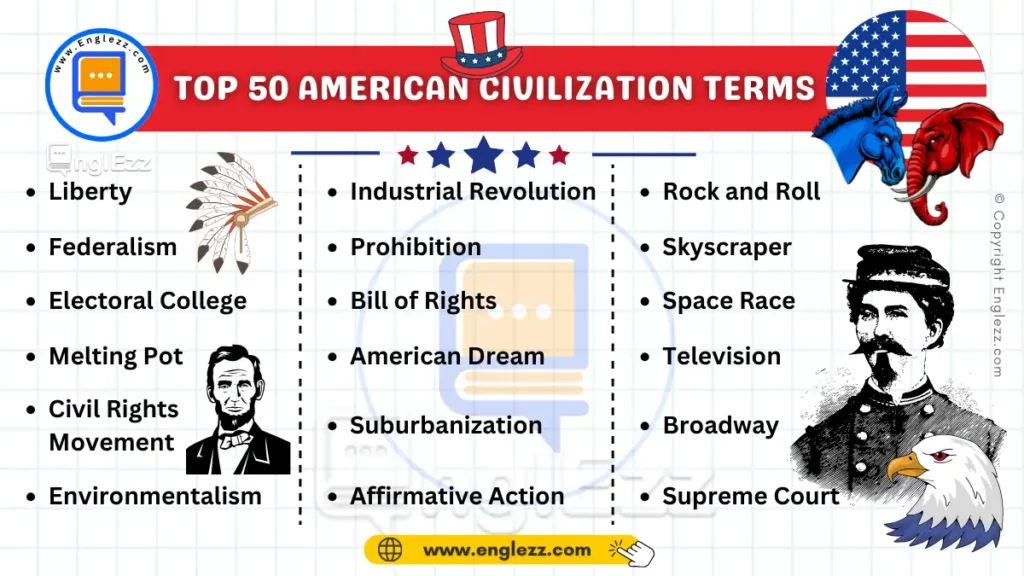
- 50 Most Common American Civilization Terms
- #1. 🏛️ Democracy
- #2. 🦅 Constitution
- #3. 🗽 Liberty
- #4. 🏛️ Federalism
- #5. 🗳️ Electoral College
- #6. 🇺🇸 Manifest Destiny
- #7. 💼 Capitalism
- #8. 🏭 Industrial Revolution
- #9. 🚫 Prohibition
- #10. 📜 Bill of Rights
- #11. 🌎 Melting Pot
- #12. 🏠 American Dream
- #13. 🚗 Suburbanization
- #14. 👥 Civil Rights Movement
- #15. 🌿 Environmentalism
- #16. 🎓 Affirmative Action
- #17. 🏛️ Checks and Balances
- #18. 🗳️ Gerrymandering
- #19. 💵 Lobbying
- #20. 🌐 Globalization
- #21. 🏛️ Separation of Church and State
- #22. 🗽 Statue of Liberty
- #23. 🦅 Bald Eagle
- #24. 🎆 Fourth of July
- #25. 🦃 Thanksgiving
- #26. 🎓 Ivy League
- #27. 🏈 Super Bowl
- #28. 🎬 Hollywood
- #29. 🍔 Fast Food
- #30. 🚗 Route 66
- #31. 🎸 Rock and Roll
- #32. 🏙️ Skyscraper
- #33. 🚀 Space Race
- #34. 📺 Television
- #35. 🎭 Broadway
- #36. 🏛️ Supreme Court
- #37. 🗳️ Filibuster
- #38. 🌽 Cornbelt
- #39. 🏛️ Capitol Hill
- #40. 🚶♂️ Civil Disobedience
- #41. 📰 Freedom of the Press
- #42. 🏠 Homestead Act
- #43. 🌊 Melting Pot vs. Salad Bowl
- #44. 🗽 Ellis Island
- #45. 🏛️ Federalist Papers
- #46. 🚗 Great Migration
- #47. 🌽 Grange Movement
- #48. 🎓 GI Bill
- #49. 🏙️ White Flight
- #50. 🗳️ Swing State
- American Civilization Terms Table
- Conclusion
50 Most Common American Civilization Terms
In this blog post, we’ll delve into a wide array of concepts that span the breadth of American history and society. From foundational political ideas to cultural phenomena, each term will be clearly defined and accompanied by its phonetic transcription to ensure proper pronunciation. Moreover, we’ll provide two practical examples for each term, illustrating how these concepts manifest in real-world situations or historical contexts.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid foundation in American civilization terminology, enabling you to engage more deeply with discussions about U.S. history, politics, and culture. Let’s embark on this educational journey through the lexicon of American civilization!
Now, let’s explore the 50 terms:
#1. 🏛️ Democracy
Definition: A system of government where power is vested in the people, who rule either directly or through freely elected representatives.
Phonetic transcription: /dɪˈmɒkrəsi/
Examples:
- The United States holds regular elections to allow citizens to choose their representatives.
- Town hall meetings provide a platform for direct democratic participation at the local level.
#2. 🦅 Constitution
Definition: The supreme law of the United States, establishing the framework for the organization of the federal government and outlining fundamental rights of citizens.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌkɒnstɪˈtjuːʃən/
Examples:
- The First Amendment to the Constitution protects freedom of speech and religion.
- The Supreme Court interprets the Constitution to determine the constitutionality of laws.
#3. 🗽 Liberty
Definition: The state of being free within society from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one’s way of life, behavior, or political views.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈlɪbərti/
Examples:
- The Statue of Liberty symbolizes the ideal of freedom for immigrants coming to America.
- Civil liberties groups work to protect individual freedoms from government overreach.
#4. 🏛️ Federalism
Definition: A system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈfedərəlɪzəm/
Examples:
- The division of powers between state and federal governments in the U.S. exemplifies federalism.
- Federal and state laws sometimes conflict, requiring courts to determine which takes precedence.
#5. 🗳️ Electoral College
Definition: The system used in U.S. presidential elections where voters in each state choose electors who then cast votes to elect the president.
Phonetic transcription: /ɪˈlektərəl ˈkɒlɪdʒ/
Examples:
- In the 2016 election, Donald Trump won the Electoral College despite losing the popular vote.
- Each state’s number of electors is equal to its total number of Senators and Representatives in Congress.
#6. 🇺🇸 Manifest Destiny
Definition: The 19th-century belief that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈmænɪfest ˈdestəni/
Examples:
- The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 greatly expanded U.S. territory, fueling the idea of Manifest Destiny.
- The concept of Manifest Destiny led to conflicts with Native American tribes as settlers moved westward.
#7. 💼 Capitalism
Definition: An economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈkæpɪtəlɪzəm/
Examples:
- The New York Stock Exchange is a symbol of American capitalism.
- Entrepreneurship and free market competition are key features of the U.S. capitalist system.
#8. 🏭 Industrial Revolution
Definition: The transition to new manufacturing processes in the period from about 1760 to sometime between 1820 and 1840.
Phonetic transcription: /ɪnˈdʌstriəl revəˈluːʃən/
Examples:
- The invention of the steam engine revolutionized transportation and manufacturing in America.
- The rise of factories during the Industrial Revolution led to urbanization and changes in labor practices.
#9. 🚫 Prohibition
Definition: The period from 1920 to 1933 when the manufacture, transportation, and sale of alcohol was banned in the United States.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌprəʊɪˈbɪʃən/
Examples:
- Speakeasies were secret bars that operated illegally during Prohibition.
- The 18th Amendment established Prohibition, while the 21st Amendment repealed it.
#10. 📜 Bill of Rights
Definition: The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution, guaranteeing specific rights and freedoms.
Phonetic transcription: /bɪl əv raɪts/
Examples:
- The Second Amendment in the Bill of Rights protects the right to bear arms.
- Freedom of the press, guaranteed by the First Amendment, allows for a free and open media.
#11. 🌎 Melting Pot
Definition: A metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous as different elements “melt together” into a harmonious whole with a common culture.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈmeltɪŋ pɒt/
Examples:
- New York City is often described as a melting pot due to its diverse immigrant populations.
- American cuisine reflects the melting pot concept, incorporating dishes from various cultures.
#12. 🏠 American Dream
Definition: The belief that anyone, regardless of their birth circumstances, can attain success and prosperity through hard work and determination.
Phonetic transcription: /əˈmerɪkən driːm/
Examples:
- Immigrants often come to the U.S. in pursuit of the American Dream.
- Owning a home is frequently cited as a key component of achieving the American Dream.
#13. 🚗 Suburbanization
Definition: The population shift from central urban areas to suburbs, typically as a result of population growth and improved transportation.
Phonetic transcription: /səˌbɜːrbənaɪˈzeɪʃən/
Examples:
- The development of highways after World War II facilitated rapid suburbanization.
- Levittown, New York, was one of the first planned suburban communities in the U.S.
#14. 👥 Civil Rights Movement
Definition: A struggle for social justice that took place mainly during the 1950s and 1960s for African Americans to gain equal rights under the law in the United States.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈsɪvəl raɪts ˈmuːvmənt/
Examples:
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech was a pivotal moment in the Civil Rights Movement.
- The Montgomery Bus Boycott was a significant protest against racial segregation in public transportation.
#15. 🌿 Environmentalism
Definition: A social movement that seeks to influence the political process by lobbying, activism, and education in order to protect natural resources and ecosystems.
Phonetic transcription: /ɪnˌvaɪrənˈmentəlɪzəm/
Examples:
- The creation of the Environmental Protection Agency in 1970 marked a significant step in American environmentalism.
- Earth Day, first celebrated in 1970, has become a global event promoting environmental awareness.
#16. 🎓 Affirmative Action
Definition: Policies that seek to increase the representation of certain groups in areas of employment, education, and culture in order to address past discrimination.
Phonetic transcription: /əˈfɜːrmətɪv ˈækʃən/
Examples:
- Many universities consider race as a factor in admissions as part of affirmative action policies.
- Some companies have diversity hiring initiatives as a form of affirmative action in the workplace.
#17. 🏛️ Checks and Balances
Definition: A system in which the different parts of government have powers that can limit or check the other parts, to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
Phonetic transcription: /tʃeks ənd ˈbælənsɪz/
Examples:
- The President can veto laws passed by Congress, but Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds majority.
- The Supreme Court can declare laws unconstitutional, providing a check on both the legislative and executive branches.
#18. 🗳️ Gerrymandering
Definition: The practice of manipulating the boundaries of electoral districts to establish a political advantage for a particular party or group.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈdʒeriˌmændərɪŋ/
Examples:
- Some states have created independent commissions to draw district lines to reduce gerrymandering.
- The term “gerrymandering” comes from Elbridge Gerry, who as governor approved a salamander-shaped district in Massachusetts.
#19. 💵 Lobbying
Definition: The act of attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, often through the provision of information or financial support.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈlɒbiɪŋ/
Examples:
- The National Rifle Association (NRA) is known for its powerful lobbying efforts on gun rights issues.
- Many large corporations maintain lobbying offices in Washington, D.C. to advocate for their interests.
#20. 🌐 Globalization
Definition: The process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide, driven by international trade and aided by information technology.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌɡləʊbəlaɪˈzeɪʃən/
Examples:
- American companies like McDonald’s and Coca-Cola have become global brands through globalization.
- The outsourcing of manufacturing jobs to other countries is a controversial aspect of globalization in the U.S.
#21. 🏛️ Separation of Church and State
Definition: The principle of keeping government and religious institutions separate and preventing the government from favoring any particular religion.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌsepəˈreɪʃən əv tʃɜːrtʃ ænd steɪt/
Examples:
- The First Amendment prohibits the establishment of an official national religion in the United States.
- Debates over prayer in public schools often center on the principle of separation of church and state.
#22. 🗽 Statue of Liberty
Definition: A colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor, symbolizing freedom and democracy.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈstætʃuː əv ˈlɪbərti/
Examples:
- The Statue of Liberty was a gift from France to the United States in 1886.
- The poem “The New Colossus” by Emma Lazarus, which includes the famous line “Give me your tired, your poor,” is inscribed on the statue’s pedestal.
#23. 🦅 Bald Eagle
Definition: The national bird and animal symbol of the United States, known for its distinctive white head and tail.
Phonetic transcription: /bɔːld ˈiːɡəl/
Examples:
- The bald eagle appears on the Great Seal of the United States.
- Conservation efforts have helped the bald eagle population recover after it was threatened by DDT use in the mid-20th century.
#24. 🎆 Fourth of July
Definition: Also known as Independence Day, a federal holiday commemorating the adoption of the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776.
Phonetic transcription: /fɔːrθ əv dʒʊˈlaɪ/
Examples:
- Fireworks displays are a common Fourth of July tradition across the United States.
- Many Americans celebrate the Fourth of July with barbecues and patriotic parades.
#25. 🦃 Thanksgiving
Definition: An annual national holiday in the United States celebrated on the fourth Thursday of November, commemorating a harvest festival celebrated by the Pilgrims in 1621.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌθæŋksˈɡɪvɪŋ/
Examples:
- Turkey is the traditional main course of most Thanksgiving dinners.
- The Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade in New York City is a popular holiday event watched by millions on television.
#26. 🎓 Ivy League
Definition: A group of eight prestigious private universities in the northeastern United States, known for their academic excellence and selective admissions.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈaɪvi liːɡ/
Examples:
- Harvard University, founded in 1636, is the oldest institution in the Ivy League.
- Ivy League schools are often associated with producing leaders in various fields, including politics and business.
#27. 🏈 Super Bowl
Definition: The annual championship game of the National Football League (NFL), one of the biggest sporting events in the United States.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈsuːpər bəʊl/
Examples:
- The Super Bowl halftime show often features performances by major music artists.
- Super Bowl Sunday has become an unofficial American holiday, with many people hosting or attending viewing parties.
#28. 🎬 Hollywood
Definition: A neighborhood in Los Angeles, California, synonymous with the American film industry.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈhɒliwʊd/
Examples:
- The Hollywood Walk of Fame honors notable figures in the entertainment industry with stars embedded in the sidewalk.
- The iconic Hollywood Sign was originally created as an advertisement for a real estate development in 1923.
#29. 🍔 Fast Food
Definition: Food that can be prepared and served quickly, often associated with chain restaurants.
Phonetic transcription: /fɑːst fuːd/
Examples:
- McDonald’s, founded in 1940, is one of the world’s largest fast-food chains.
- Drive-thru service, popularized by fast-food restaurants, has become a common feature of American car culture.
#30. 🚗 Route 66
Definition: One of the original highways in the U.S. Highway System, running from Chicago to Los Angeles, often called “The Mother Road.”
Phonetic transcription: /ruːt ˈsɪksti sɪks/
Examples:
- Route 66 played a significant role in the westward migration during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s.
- Many historic landmarks and businesses along Route 66 have become tourist attractions, preserving a slice of Americana.
#31. 🎸 Rock and Roll
Definition: A genre of popular music that originated in the United States in the 1950s, characterized by electric guitars, strong rhythms, and often youth-oriented lyrics.
Phonetic transcription: /rɒk ənd rəʊl/
Examples:
- Elvis Presley, often called “The King of Rock and Roll,” helped popularize the genre in the 1950s.
- The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in Cleveland, Ohio, honors influential figures in the development of rock music.
#32. 🏙️ Skyscraper
Definition: A very tall, continuously habitable building with multiple floors, typically associated with urban development in American cities.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈskaɪskreɪpər/
Examples:
- The Empire State Building in New York City was the world’s tallest building for nearly 40 years.
- Chicago’s Home Insurance Building, completed in 1885, is often considered the world’s first modern skyscrapers
#33. 🚀 Space Race
Definition: The competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to achieve superiority in space exploration during the Cold War era.
Phonetic transcription: /speɪs reɪs/
Examples:
- The Apollo 11 mission, which landed humans on the moon in 1969, was a major American victory in the Space Race.
- NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) was established in 1958 as a direct response to the Space Race.
#34. 📺 Television
Definition: An electronic system of transmitting transient images and sound into a device that displays them, which became a dominant form of mass media in the United States.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈtelɪvɪʒən/
Examples:
- The “I Love Lucy” show in the 1950s was one of the first television programs to be filmed in front of a live studio audience.
- The televised Kennedy-Nixon debates in 1960 demonstrated the power of television in shaping public opinion during elections.
#35. 🎭 Broadway
Definition: A street in New York City known for its theatrical performances, often used as a metonym for the American theater industry.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈbrɔːdweɪ/
Examples:
- “Hamilton,” a Broadway musical about American Founding Father Alexander Hamilton, became a cultural phenomenon in the 2010s.
- The Tony Awards annually recognize excellence in live Broadway theater.
#36. 🏛️ Supreme Court
Definition: The highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States, responsible for interpreting the Constitution and federal laws.
Phonetic transcription: /sʊˈpriːm kɔːrt/
Examples:
- The landmark case Brown v. Board of Education (1954) saw the Supreme Court rule that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional.
- Supreme Court justices are appointed for life by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
#37. 🗳️ Filibuster
Definition: A political procedure where one or more members of parliament or congress debate over a proposed piece of legislation to delay or entirely prevent a decision being made on the proposal.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈfɪlɪbʌstər/
Examples:
- In 1957, Strom Thurmond conducted the longest individual filibuster in Senate history, speaking for over 24 hours against the Civil Rights Act.
- The Senate’s cloture rule, requiring 60 votes to end a filibuster, has become a significant factor in modern legislative debates.
#38. 🌽 Cornbelt
Definition: A region in the Midwestern United States where corn is a major crop, typically including Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, and parts of surrounding states.
Phonetic transcription: /kɔːrn belt/
Examples:
- The Cornbelt plays a crucial role in U.S. agriculture and is often referred to as America’s breadbasket.
- Iowa, a key state in the Cornbelt, is famous for hosting the first caucuses in the U.S. presidential primary season.
#39. 🏛️ Capitol Hill
Definition: A metonym for the United States Congress and the legislative branch of the U.S. government, named after the Capitol building in Washington, D.C.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈkæpɪtəl hɪl/
Examples:
- Lobbyists often work on Capitol Hill to influence legislation.
- The State of the Union address is delivered annually by the President to a joint session of Congress on Capitol Hill.
#40. 🚶♂️ Civil Disobedience
Definition: The active, professed refusal to obey certain laws, demands, or commands of a government, or of an occupying international power.
Phonetic transcription: /ˌsɪvəl dɪsəˈbiːdiəns/
Examples:
- Rosa Parks’ refusal to give up her bus seat to a white passenger in 1955 was an act of civil disobedience that helped spark the Civil Rights Movement.
- The sit-ins at segregated lunch counters in the 1960s were a form of civil disobedience used to protest racial discrimination.
#41. 📰 Freedom of the Press
Definition: The principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic media, should be considered a right to be exercised freely.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈfriːdəm əv ðə pres/
Examples:
- The Pentagon Papers case in 1971 reaffirmed the importance of freedom of the press in reporting on government activities.
- The First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution protects freedom of the press from government interference.
#42. 🏠 Homestead Act
Definition: A United States federal law that gave an applicant ownership of land, typically 160 acres of undeveloped federal land west of the Mississippi River.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈhoʊmsted ækt/
Examples:
- The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged Western migration and settlement in the United States.
- Under the Homestead Act, settlers were required to live on and improve the land for five years before gaining full ownership.
#43. 🌊 Melting Pot vs. Salad Bowl
Definition: Two contrasting metaphors for how immigrants integrate into American society: the melting pot suggests assimilation, while the salad bowl implies maintaining distinct cultural identities.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈmeltɪŋ pɒt vs ˈsæləd boʊl/
Examples:
- The melting pot theory was popularized in the early 20th century, emphasizing the blending of cultures.
- The salad bowl concept gained prominence in the late 20th century, celebrating cultural diversity within American society.
#44. 🗽 Ellis Island
Definition: A former immigration inspection station in New York Harbor, through which millions of immigrants entered the United States from 1892 to 1954.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈelɪs ˈaɪlənd/
Examples:
- Over 12 million immigrants were processed at Ellis Island during its years of operation.
- The Ellis Island National Museum of Immigration now stands as a reminder of America’s immigrant heritage.
#45. 🏛️ Federalist Papers
Definition: A collection of 85 articles and essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay to promote the ratification of the United States Constitution.
Phonetic transcription: /ˈfedərəlɪst ˈpeɪpərz/
Examples:
- Federalist No. 10, written by James Madison, addresses the dangers of factions in a democracy.
- The Federalist Papers are still frequently cited in constitutional law cases and debates.
#46. 🚗 Great Migration
Definition: The movement of six million African Americans from the rural Southern United States to the urban Northeast, Midwest, and West between 1916 and 1970.
Phonetic transcription: /ɡreɪt maɪˈɡreɪʃən/
Examples:
- The Great Migration led to significant demographic changes in cities like Chicago, Detroit, and New York.
- The Harlem Renaissance, a cultural movement in the 1920s, was partly fueled by the Great Migration.
#47. 🌽 Grange Movement
Definition: A social movement among U.S. farmers in the late 19th century to promote direct marketing of farm products and reform of railroad regulations.
Phonetic transcription: /ɡreɪndʒ ˈmuːvmənt/
Examples:
- The National Grange of the Order of Patrons of Husbandry, founded in 1867, was a key organization in the Grange Movement.
- The Grange Movement led to the passage of state laws regulating railroad freight rates.
#48. 🎓 GI Bill
Definition: A law that provided a range of benefits for returning World War II veterans, including low-cost mortgages, low-interest loans to start a business, and payments of tuition and living expenses to attend university.
Phonetic transcription: /dʒiː aɪ bɪl/
Examples:
- The original GI Bill, signed into law in 1944, helped millions of veterans attend college and buy homes.
- The Post-9/11 GI Bill, enacted in 2008, extended similar benefits to veterans of more recent conflicts.
#49. 🏙️ White Flight
Definition: The migration of white people from racially mixed urban areas to more racially homogeneous suburban areas.
Phonetic transcription: /waɪt flaɪt/
Examples:
- White flight in the 1950s and 1960s contributed to the racial segregation of many American cities.
- The phenomenon of white flight often led to decreased tax revenues and declining public services in urban areas.
#50. 🗳️ Swing State
Definition: A state where the two major political parties have similar levels of support among voters, viewed as important in determining the outcome of a presidential election.
Phonetic transcription: /swɪŋ steɪt/
Examples:
- Florida has been considered a crucial swing state in recent presidential elections.
- Presidential candidates often focus their campaign efforts on swing states to maximize their chances of winning the Electoral College.
American Civilization Terms Table
| Democracy | Manifest Destiny | Fast Food |
| Constitution | Capitalism | Route 66 |
| Liberty | Industrial Revolution | Rock and Roll |
| Federalism | Prohibition | Skyscraper |
| Electoral College | Bill of Rights | Space Race |
| Melting Pot | American Dream | Television |
| Civil Rights Movement | Suburbanization | Broadway |
| Environmentalism | Affirmative Action | Supreme Court |
| Checks and Balances | Gerrymandering | Filibuster |
| Lobbying | Globalization | Cornbelt |
Conclusion
As we conclude our journey through these 50 essential American civilization terms, it’s clear that the tapestry of U.S. history and culture is rich, complex, and continually evolving. From the foundational principles of democracy and liberty to the cultural phenomena that shape everyday life, these terms offer a window into the American experience.
Understanding these concepts is crucial not only for students of American history but for anyone seeking to grasp the nuances of U.S. society. They provide context for current events, illuminate the roots of ongoing debates, and highlight the values that have shaped the nation’s trajectory.
However, it’s important to remember that American civilization is not static. New terms and concepts continue to emerge as the country faces fresh challenges and opportunities. The ongoing discussions about topics like social justice, technological impact, and global interconnectedness are shaping new vocabularies and redefining existing ones.
By familiarizing ourselves with these terms and their real-world applications, we equip ourselves to engage more meaningfully with American culture, politics, and society. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply a curious individual, this knowledge serves as a foundation for deeper understanding and more informed participation in the ongoing American story.







Unlock the essence of American culture with our bite-sized guide to 50 key terms!
🗽 From politics to pop culture, master these concepts and impress your friends. Want more language hacks? Follow @EnglEzz for daily doses of linguistic brilliance! 🚀 Check out the full post at and level up your English game! 💪
.
https://www.englezz.com/most-common-american-civilization-terms/
.
#englezz #vocabulary #linguistics #americanculture #englishlearning #historyterms #languagehacks #esl #americanhistory