In recent years, virtual learning has become an increasingly popular way of acquiring knowledge and skills. With the advent of advanced technology, people now have access to a wealth of educational resources right at their fingertips. This shift towards virtual learning has transformed the traditional education landscape, offering flexibility and accessibility that was previously unimaginable.
Table of Contents
- Pros And Cons Of Virtual Learning: Your Ultimate Guide
- Definition of Virtual Learning
- Evolution of Virtual Learning in Education
- Pros of Virtual Learning
- III. Cons of Virtual Learning
- IV. Quality of Learning Experience
- V. Student Engagement and Motivation
- VI. Impact on Traditional Educational Models
- VII. Future Trends in Virtual Learning
- VIII. Legal and Ethical Considerations:
- IX. Recommendations for Successful Virtual Learning Implementation
- Final Thoughts
Pros And Cons Of Virtual Learning: Your Ultimate Guide
Virtual learning encompasses a wide range of formats, from online courses and webinars to interactive modules and virtual classrooms. Thanks to this diversity, individuals are able to tailor their learning experiences according to their specific needs and preferences. The convenience of being able to learn from anywhere with an internet connection has undoubtedly broken down barriers for many learners who may have previously struggled with traditional in-person classes due to geographical constraints or time limitations.
Definition of Virtual Learning
Virtual learning, also known as online learning or e-learning, refers to the process of acquiring knowledge or skills through digital platforms and resources. This mode of education utilizes various technologies such as video conferencing, online forums, and educational apps to deliver content, facilitate discussions, and assess student progress. Unlike traditional face-to-face instruction, virtual learning offers flexibility and convenience as students can access materials and participate in activities from any location with internet connectivity.

One of the defining features of virtual learning is its adaptability to diverse learning styles and preferences. Students have the freedom to customize their study environment, pace their learning according to individual needs, and engage with multimedia content that caters to visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learners. Moreover, virtual learning can break down geographical barriers by connecting students from different parts of the world for collaborative projects or discussions.
This global perspective not only enriches the educational experience but also fosters cross-cultural understanding and collaboration – an invaluable skill in today’s interconnected world.
Evolution of Virtual Learning in Education
The evolution of virtual learning in education has been a remarkable journey marked by rapid technological advancements and shifting educational paradigms. Initially, virtual learning was primarily confined to simple online courses and webinars, but it has since transformed into a multifaceted platform that offers immersive experiences through virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. These innovations have enabled students to engage with course materials in entirely new ways, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in virtual learning has revolutionized personalized education by analyzing individual learning patterns and providing tailored recommendations for improvement. This adaptive learning approach not only caters to diverse student needs but also ensures that each student progresses at their own pace. Moreover, the pandemic-induced surge in remote learning has propelled the development of collaborative tools, making group projects and discussions more seamless within virtual environments.
As we continue to embrace these technological advancements, it’s clear that the evolution of virtual learning holds immense potential for reshaping the future of education by creating dynamic and interactive learning experiences for students worldwide.
Pros of Virtual Learning
Virtual learning offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling students to access educational resources from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for individuals with busy schedules, allowing them to balance work, family, and other commitments while pursuing their education. Additionally, virtual learning provides the opportunity for personalized learning experiences through adaptive software and interactive multimedia resources. Students can learn at their own pace and revisit material as needed, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
Another key benefit of virtual learning is the potential for global connectivity and collaboration. Through online platforms, students can engage in discussion forums, collaborate on projects, and interact with peers from around the world. This not only broadens students’ perspectives but also fosters a sense of global citizenship and cultural awareness. Furthermore, virtual learning encourages the development of digital literacy skills that are essential in today’s technology-driven society, preparing students for success in a rapidly evolving workforce.
A. Flexibility and Convenience
In the realm of virtual learning, one cannot overlook the unparalleled advantage of flexibility and convenience it offers. Students are no longer bound by rigid schedules or geographic limitations, allowing them to tailor their learning experience to suit their unique needs and lifestyles. Whether it’s fitting in coursework around work commitments, family obligations, or personal hobbies, online platforms provide the freedom to learn at one’s own pace and in a location of their choice.
The adaptability of virtual learning also extends to the array of resources and tools available at students’ fingertips. From video lectures and interactive simulations to digital libraries and collaborative online forums, learners have access to a wealth of educational materials that can enhance their understanding beyond traditional textbooks.
With assignments and assessments often being conducted digitally as well, individuals can conveniently submit work remotely without the constraints of physical attendance or paper submissions. Ultimately, this infusion of flexibility into academic pursuits has revolutionized the way we approach education, offering an enticing avenue for personalized growth and exploration.
1. Asynchronous Learning Opportunities
Asynchronous learning opportunities have become an integral part of modern virtual education. Students are no longer confined by traditional classroom schedules, allowing them to access course materials and lectures at their own convenience. This flexibility empowers learners to balance their studies with other responsibilities, making education more accessible than ever before. Additionally, asynchronous learning promotes self-discipline and time management skills as students take ownership of their learning pace.
Furthermore, this approach encourages a diverse range of perspectives and ideas as students engage in discussions across different time zones and personal schedules. The varied input enhances the overall learning experience, promoting critical thinking and empathy as individuals consider viewpoints outside of their immediate environment. Asynchronous learning fosters a sense of global connectivity, preparing students for an interconnected world where collaboration and adaptability are essential skills for success.
2. Customized Learning Paths
Customized learning paths have revolutionized the virtual learning landscape by catering to individual needs and preferences. Instead of following a one-size-fits-all curriculum, students can now personalize their educational journey based on their interests, goals, and learning styles. This approach not only fosters a deeper understanding of the material but also promotes a sense of ownership and accountability for one’s own learning.
Furthermore, customized learning paths have the potential to address the diverse needs of students with varying abilities and backgrounds. By allowing individuals to progress at their own pace and focus on specific areas that require attention, virtual learners are provided with a more inclusive and equitable education experience. This tailored approach acknowledges that every student’s journey is unique, ultimately leading to improved engagement and motivation in the virtual classroom setting.
B. Accessibility and Inclusivity
Accessibility and inclusivity are crucial aspects to consider when analyzing the pros and cons of virtual learning. While virtual learning has made education more accessible to many individuals, it is important to address the potential digital divide that may exclude those without access to necessary technology or reliable internet. Inclusivity also pertains to accommodating diverse learners, including those with disabilities who may require specialized tools or accommodations in a virtual setting. However, virtual learning can also offer unique opportunities for inclusivity by providing flexibility for students with various needs and creating an environment where different perspectives can thrive.
Furthermore, incorporating universal design principles in virtual learning platforms can enhance accessibility for all users, not just those with disabilities. Prioritizing captioning, screen-reader compatibility, and adjustable font sizes can remove barriers and ensure that everyone has equal access to educational materials. Embracing accessibility and inclusivity in virtual learning not only benefits individual learners but also enriches the overall educational experience by fostering a welcoming and supportive environment for all participants.
1. Overcoming Geographical Barriers
With the rise of virtual learning, overcoming geographical barriers has become more achievable than ever before. Students now have the opportunity to access educational resources and interact with experts from around the world without being limited by their location. This not only provides a diverse and enriching learning experience but also allows students to be exposed to different perspectives and cultures, broadening their understanding of the world.
Moreover, virtual learning enables individuals in remote or underserved areas to have access to high-quality education that they may not have had otherwise. This level of inclusivity is particularly significant as it levels the playing field for students from all backgrounds and locations. By transcending geographical limitations, virtual learning empowers students to pursue their academic goals regardless of where they are located, fostering a more equitable education system overall.
2. Catering to Diverse Learning Styles
When it comes to virtual learning, catering to diverse learning styles is both a challenge and an opportunity. The traditional one-size-fits-all approach no longer suffices in our modern, technologically advanced society. Educators must now explore adaptive strategies that appeal to visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile learners alike. Employing multimedia presentations, interactive simulations, and real-world case studies can help accommodate various learning preferences and enhance overall engagement.
Furthermore, offering personalized learning paths based on individual strengths and weaknesses can be a game-changer for virtual education. By leveraging technology to identify students’ unique learning styles and tailor content delivery accordingly, instructors can better support diverse needs within the digital classroom. This proactive approach not only fosters inclusivity but also maximizes the potential for student success in virtual settings.
C. Technological Integration
Technological integration is revolutionizing virtual learning with the potential to personalize and enhance educational experiences. The ability to integrate interactive technologies like virtual reality and artificial intelligence enables students to immerse themselves in dynamic learning environments, making complex concepts more tangible and engaging. Furthermore, technology facilitates the integration of data analytics, enabling educators to track student progress in real-time and provide targeted support where needed.

However, as we embrace technological integration in virtual learning, it’s essential to address concerns about over-reliance on digital tools. While technology can enrich the educational landscape, it’s crucial to strike a balance that preserves human interaction and fosters critical thinking skills. Additionally, ensuring equal access to technology for all students is vital in avoiding exacerbating inequalities within education.
1. Interactive Multimedia Resources
Interactive multimedia resources have revolutionized the landscape of virtual learning, offering a diverse array of dynamic content that caters to different learning styles. Through engaging videos, simulations, and interactive applications, students can fully immerse themselves in the subject matter, making the learning process more captivating and effective. Furthermore, these resources enable personalized learning experiences by allowing students to progress at their own pace and explore topics in an interactive manner that fosters deeper understanding.
In addition to enhancing engagement and personalization, interactive multimedia resources also facilitate collaboration and communication among students and educators. With virtual classrooms equipped with chat features, video conferencing capabilities, and collaborative tools, learners can actively participate in discussions and group projects.
This dynamic interaction not only mirrors real-life social settings but also cultivates essential 21st-century skills such as teamwork, communication, and digital literacy. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the potential for interactive multimedia resources to enrich the virtual learning experience for all involved.
2. Real-time Data Analytics for Adaptive Learning
Real-time data analytics is revolutionizing the landscape of adaptive learning in virtual education. By harnessing the power of real-time data, educators can gain valuable insights into each student’s learning journey, allowing for personalized and adaptive learning experiences. This dynamic approach enables educators to identify areas where students may be struggling and provide targeted support, ultimately leading to improved learning outcomes.
Furthermore, real-time data analytics paves the way for predictive modeling, helping educators anticipate students’ future needs and adapt their teaching strategies accordingly. With this proactive approach, virtual learning becomes more intuitive and responsive to individual student requirements. By analyzing real-time data on factors such as engagement levels, progress, and areas of difficulty, educators can tailor their instructional materials and interventions in a timely manner, enhancing the overall efficiency of virtual learning environments.
D. Cost Efficiency
One of the most compelling aspects of virtual learning is its cost efficiency. Traditional education often comes with significant expenses such as commuting, textbooks, and accommodation. With virtual learning, however, these costs are greatly reduced or even eliminated entirely. Students can save money on transportation and housing since they can attend classes from the comfort of their own homes. Additionally, digital materials are often more affordable than physical textbooks, leading to further cost savings for students.
Moreover, virtual learning also benefits educational institutions by reducing overhead costs associated with maintaining physical facilities. This means that resources can be reallocated toward improving the quality of online courses and providing additional support services for students. As a result, both learners and educational institutions stand to benefit from the increased cost efficiency provided by virtual learning platforms.
1. Reduction in Physical Infrastructure Costs
One of the most significant advantages of virtual learning is the reduction in physical infrastructure costs. Traditional educational institutions often face substantial expenses related to maintaining physical classrooms, facilities, and equipment. With virtual learning, these costs diminish significantly as there is no need for extensive campus real estate, maintenance of buildings, or utility expenses. This cost reduction can result in more affordable education for students and lower operational overheads for educational organizations.
Moreover, the shift to virtual learning allows schools and universities to reallocate budget previously used for physical infrastructure towards enhancing digital resources and technology integration. This can lead to a more enriching and interactive learning experience for students through investments in advanced software platforms, online libraries, and multimedia content. Additionally, reducing physical infrastructure costs promotes environmental sustainability by decreasing energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with traditional campuses. By embracing virtual learning environments, institutions can not only save money but also contribute positively to environmental conservation efforts.
2. Accessibility to Open Educational Resources
Accessibility to Open Educational Resources (OER) has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of virtual learning, offering a wealth of knowledge at no cost. OER opens the door to a vast array of educational materials, including textbooks, videos, and lectures, empowering learners with diverse resources that cater to individualized learning styles. By breaking down financial barriers and promoting inclusivity, OER allows virtually anyone with an internet connection to access high-quality educational content from esteemed institutions around the world.
Furthermore, the flexibility provided by OER enables learners to study at their own pace and customize their learning experience according to their specific needs. This accessibility not only benefits traditional students but also serves non-traditional learners such as adult education seekers and independent learners. In addition, OER presents a valuable opportunity for educators to adapt and remix content according to different teaching styles and student requirements.
With easy accessibility comes unprecedented potential for collaboration among educators who can share innovative approaches and resources across borders without geographic limitations or restrictive licensing barriers.
III. Cons of Virtual Learning
Virtual learning offers a plethora of benefits, but it also has its downsides. One significant disadvantage is the lack of face-to-face interaction. Students may find it challenging to build meaningful connections with their peers and instructors, leading to feelings of isolation and disengagement. Additionally, virtual learning can be detrimental to students’ mental and emotional well-being as they miss out on the social aspects of traditional classroom settings.
Another drawback of virtual learning is the potential for technological issues. Students may encounter internet connectivity problems, software glitches, or device malfunctions that disrupt their learning experience. These technical challenges can cause frustration and hinder students’ ability to participate fully in online classes. Furthermore, excessive screen time associated with virtual learning can have adverse effects on students’ physical health, leading to eye strain, headaches, and overall fatigue.
A. Technological Barriers
Technological barriers have emerged as a significant hurdle in the transition to virtual learning. While online education offers flexibility and accessibility, it can also exacerbate inequalities. Students from lower-income households may lack access to high-speed internet or reliable devices, hindering their ability to fully engage with virtual lessons. Additionally, the reliance on digital platforms demands a level of technological proficiency that some students and educators may not possess.
Moreover, the rapid evolution of technology presents an ongoing challenge for educational institutions. The need to constantly update software and hardware can strain already limited resources. Furthermore, technical issues such as connectivity problems or software malfunctions can disrupt the flow of virtual classes, leading to frustration for both educators and students alike. As we continue to navigate this new educational landscape, it’s crucial to address these technological barriers in order to create a more equitable and inclusive virtual learning environment for all.
1. Limited Access to High-speed Internet
Limited access to high-speed internet has become a significant barrier to virtual learning for many students. The digital divide, exacerbated by socioeconomic disparities, leaves students from underserved communities at a disadvantage. Without high-speed internet, these students are unable to fully engage in online classes, access educational resources, or participate in interactive learning activities. This not only widens the achievement gap but also hinders these students’ ability to compete on an equal footing with their more privileged peers.

Furthermore, the lack of high-speed internet access can result in frustration and mental disengagement among students who struggle with slow or unreliable connections. This can lead to decreased motivation and productivity, affecting their overall academic performance. Additionally, educators may find it challenging to deliver quality instruction when some of their students are hampered by insufficient internet access, further complicating the transition to virtual learning for both teachers and learners alike.
2. Disparities in Device Availability
Disparities in device availability have become a significant obstacle in the transition to virtual learning. While some students have access to high-quality computers and reliable internet, others are left struggling with outdated devices or no device at all. This digital divide is widening educational inequities, as students from lower-income households are at a disadvantage when it comes to accessing online resources and participating in virtual classes.
Furthermore, the disparities in device availability amplify existing social and economic inequalities. Students who lack access to suitable devices often face difficulties completing assignments, attending virtual lectures, or engaging in collaborative projects. As a result, the gap between privileged and marginalized students continues to widen, creating long-term consequences for their academic success and future prospects. It is crucial for educators and policymakers alike to address these disparities head-on in order to ensure equal opportunities for all students in the virtual learning environment.
B. Lack of Social Interaction
As much as virtual learning has its benefits, it also comes with a significant drawback: the lack of social interaction. While students can connect digitally, the absence of in-person interactions can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. This lack of face-to-face communication can hinder the development of important social skills such as active listening, conflict resolution, and teamwork.
Additionally, the absence of physical proximity can impact students’ emotional well-being. Without regular social engagement, students may struggle to form meaningful connections, resulting in increased feelings of disconnect and disengagement from their peers. The implications for mental health cannot be ignored; prolonged lack of social interaction can contribute to anxiety and depression among young learners.
1. Impact on Social and Emotional Development
The impact of virtual learning on social and emotional development is a topic that has sparked much debate. On one hand, some argue that remote education provides a more comfortable environment for students to express themselves and engage with their peers without the pressure of face-to-face interactions. However, the lack of in-person connection can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, potentially hindering the development of crucial interpersonal skills.
Furthermore, virtual learning may affect students’ ability to develop empathy and understanding towards others as they miss out on nonverbal cues and subtle social interactions present in a traditional classroom setting. The absence of real-time feedback from teachers and classmates might also affect students’ self-esteem and confidence, potentially impacting their emotional well-being. As schools continue to navigate between physical classrooms and virtual settings, it becomes increasingly important to carefully consider the long-term effects of this shift on students’ social and emotional growth.
2. Challenges in Building Peer Relationships
Building peer relationships is a crucial aspect of personal and social development, but it doesn’t come without its challenges. In the virtual learning landscape, students are faced with obstacles in establishing meaningful connections with their peers. The absence of face-to-face interaction and non-verbal cues makes it difficult to gauge emotions and build rapport. Additionally, the lack of physical presence can lead to feelings of isolation and disconnect, ultimately hindering the natural flow of building genuine peer relationships.
Furthermore, virtual learning platforms may not always incorporate effective tools for students to engage in group activities or discussions, making it challenging for them to collaborate and connect with their peers on a deeper level. This limitation in real-time interaction could potentially hinder the development of essential social skills that are typically nurtured through regular in-person interactions. As a result, students may miss out on valuable opportunities to develop empathy, communication skills, and conflict resolution abilities within peer relationships.
C. Potential for Distractions
One of the major drawbacks of virtual learning is the potential for distractions. With access to their personal devices and home environment, students may find it challenging to maintain focus during online classes. Social media notifications, household chores, and family members can all serve as distractions that hinder a student’s ability to fully engage with their coursework.
Moreover, the lack of physical presence and accountability in a traditional classroom setting can make it easier for students to become disengaged or lose motivation in a virtual learning environment. The absence of direct supervision from instructors can also contribute to an increase in distractions for some learners. It’s important for educators and students alike to recognize these potential distractions and work together to find effective strategies for minimizing their impact on the learning process.
1. Home Environment Impact on Focus
The impact of the home environment on focus cannot be overstated, especially in the context of virtual learning. Sudden shifts from school to home can disrupt focus, with various distractions like noise, family members, and household chores vying for attention. On the flip side, a conducive home environment can significantly boost focus levels. By creating designated study areas and setting boundaries, students can cultivate a space that promotes deep concentration and reduces external disruptions.
Furthermore, incorporating elements such as natural light and greenery into the home environment has been shown to enhance cognitive function and productivity. A clutter-free workspace and comfortable seating arrangements also play a crucial role in fostering focus during virtual learning sessions. Understanding these nuances allows individuals to tailor their surroundings to support maximum concentration and ultimately improve their overall learning experience.
2. Technological Distractions during Learning
In today’s digitally connected world, technology offers a multitude of benefits to the educational landscape. However, it also presents significant distractions that can hinder the learning process. From social media notifications to endless YouTube videos and tempting online games, the allure of technology can divert students’ attention away from their studies. This constant battle for focus can lead to decreased productivity and lower academic performance if not managed effectively.
Moreover, the seamless integration of technology into virtual learning environments has blurred the lines between educational tools and recreational devices. While access to information has become more convenient than ever, learners may find themselves navigating a delicate balance between utilizing technological resources for education and succumbing to its entertaining distractions.
As such, educators must be proactive in implementing strategies that promote mindfulness, discipline, and responsible usage of technology in order to foster an effective learning environment amidst these potential disruptions.
D. Instructor-Student Interaction Challenges
Instructor-Student Interaction Challenges in virtual learning present a complex dynamic that requires special attention. One key challenge is establishing a sense of connection and engagement in the absence of physical presence. Without face-to-face interaction, instructors may struggle to gauge student understanding or provide personalized feedback effectively, leading to potential gaps in learning. Additionally, maintaining motivation and focus in an online environment can be challenging for both students and instructors, as distractions are more prevalent and the sense of accountability can be diminished.

Moreover, the technological barriers inherent in virtual learning can also hinder effective instructor-student interaction. Glitches, connectivity issues, or unfamiliarity with digital tools may disrupt communication and lead to frustration on both sides. This underscores the need for adaptable teaching approaches that accommodate diverse technological literacy levels among students while also providing adequate support from instructional staff.
1. Difficulty in Providing Immediate Clarifications
It’s no secret that virtual learning has revolutionized education, but it comes with its own set of challenges. One notable difficulty is providing immediate clarifications to students during online classes. Unlike traditional in-person learning, where students can simply raise their hands and ask questions, virtual classrooms often face communication barriers that make immediate clarity hard to achieve. Factors like internet connectivity issues, time zone differences, and technical glitches can hinder real-time interaction between teachers and students.
Furthermore, in a virtual setting, the absence of non-verbal cues makes it even more challenging to gauge if a student has truly understood the material being taught. This lack of immediate feedback can lead to misunderstandings and misconceptions going unaddressed for longer periods. As educators continue to adapt to this new learning landscape, finding creative solutions for providing on-the-spot clarifications becomes increasingly crucial for maintaining the quality of education in a virtual environment.
2. Potential for Miscommunication in Virtual Spaces
In the dynamic realm of virtual spaces, miscommunication can lurk around unexpected corners, presenting a formidable challenge to effective learning. The absence of nonverbal cues and physical presence in virtual interactions can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. Additionally, technical glitches such as poor audio quality or delayed responses can further compound communication barriers.
Furthermore, the lack of immediate feedback in virtual spaces can exacerbate the potential for miscommunication. In face-to-face interactions, individuals can gauge reactions in real-time and adjust their communication accordingly. However, in virtual environments, this instantaneous feedback loop may be disrupted or lost entirely. As a result, participants may struggle to convey their intended message clearly or accurately interpret the messages of others.
IV. Quality of Learning Experience
The quality of the learning experience in a virtual setting is influenced by various factors, including technology, teaching methods, and student engagement. While virtual learning offers flexibility and convenience, it can also present challenges in terms of personalized interaction between students and teachers. One key advantage is the ability to cater to diverse learning styles through multimedia tools and interactive platforms, fostering a more dynamic educational experience.
Moreover, the adaptability of virtual learning allows for real-time feedback and evaluation, enabling educators to tailor their approach to meet individual student needs more effectively. However, there are potential drawbacks related to the lack of physical presence and non-verbal cues that are essential for building rapport and understanding among peers. Despite these hurdles, innovation in virtual learning tools continues to enhance the quality of the overall educational experience.
In essence, while virtual learning has its limitations compared to traditional classroom settings, it also presents opportunities for creativity and resourcefulness in delivering high-quality education. By leveraging advanced technology alongside thoughtful pedagogy, educators can optimize the quality of the online learning experience while addressing its inherent challenges.
A. Adaptability of Virtual Learning Platforms
One of the most captivating aspects of virtual learning platforms is their remarkable adaptability. These digital tools have the inherent ability to accommodate diverse learning styles and needs, offering flexibility in terms of pace, schedule, and mode of delivery. For example, students with different learning paces can progress at their own speed, while those juggling work and family commitments can access materials at any time that suits them best. Furthermore, virtual platforms allow for seamless integration of multimedia elements such as videos, interactive simulations, and audio recordings, enhancing engagement and accessibility for all types of learners.
In addition to individual adaptability, virtual learning platforms also possess the potential to evolve rapidly in response to changing educational needs. The dynamic nature of these technologies means that new features can be continually added to improve usability and enhance the overall learning experience. This adaptability ensures that educators are equipped with cutting-edge resources that meet evolving pedagogical requirements and embrace diverse teaching methodologies.
As a result, virtual learning platforms remain at the forefront of innovation within the education sector by accommodating emerging trends such as gamification, collaborative tools, and augmented reality applications—ultimately enhancing student engagement and knowledge acquisition.
1. Responsive Design for Varied Devices
Responsive design for varied devices has become a fundamental aspect of virtual learning, ensuring seamless access to educational content across different platforms. With the increasing prevalence of smartphones, tablets, and laptops in the educational landscape, it’s crucial for content to adapt to various screen sizes and resolutions. This not only enhances the user experience but also accommodates different learning styles and preferences. By employing responsive design principles, educators can cater to a diverse audience and create an inclusive virtual learning environment.
However, while responsive design offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Ensuring consistent user experience across devices requires meticulous testing and optimization, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Additionally, accommodating varied device capabilities may necessitate trade-offs in visual elements or functionality. Despite these challenges, prioritizing responsive design is essential for delivering an effective virtual learning experience that caters to the needs of modern students who engage with educational content through a wide range of devices.
2. User-Friendly Interface
The significance of a user-friendly interface in virtual learning cannot be understated. A well-designed interface enhances the overall learning experience by providing an intuitive and easily navigable platform for students. User-friendly interfaces contribute to higher levels of student engagement, as they allow users to access course materials, submit assignments, and interact with peers and instructors seamlessly. By reducing the complexity of the learning platform, students can focus more on the actual content being taught rather than struggling with cumbersome interfaces.
Furthermore, a user-friendly interface promotes inclusivity by making virtual learning accessible to students with various technical abilities. It empowers learners to take control of their education without feeling overwhelmed by complicated systems. Additionally, a streamlined interface fosters efficiency in communication and collaboration among students and instructors, ultimately enriching the educational experience. As technology continues to play an integral role in education, prioritizing user-friendly interfaces is paramount for ensuring that virtual learning remains engaging and accessible for all learners.
B. Pedagogical Effectiveness
Leveraging technology in the virtual learning environment can significantly enhance pedagogical effectiveness by providing personalized learning experiences. With the use of adaptive learning platforms, educators can tailor content and teaching methods to suit individual student needs, accelerating their progress and understanding. Furthermore, virtual simulations and interactive multimedia tools offer immersive experiences that cater to various learning styles, enhancing conceptual understanding and retention. This level of personalization enables students to engage more deeply with the material, fostering a greater sense of empowerment and autonomy in their education.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that while virtual learning offers expansive opportunities for pedagogical effectiveness, it also presents challenges in maintaining student engagement. Without face-to-face interaction, educators need to be particularly vigilant in employing diverse strategies to sustain motivation and participation. Implementing collaborative virtual activities and real-world applications can bridge this gap by instilling a sense of community among students while reinforcing practical comprehension. Therefore, harnessing a multifaceted approach in digital pedagogy is essential for ensuring sustained engagement throughout the virtual learning experience.
1. Integration of Active Learning Strategies
Active learning strategies have become increasingly critical in the virtual learning environment as educators seek to engage students in more meaningful ways. One effective approach is the use of problem-based learning, allowing students to grapple with real-world scenarios and apply their knowledge to practical situations. By integrating collaborative activities such as group discussions and projects, virtual classrooms can emulate the interactive nature of traditional settings, fostering teamwork and critical thinking skills.
Furthermore, incorporating experiential learning techniques like simulations and role-playing exercises can bring a dynamic dimension to online education. These methods provide valuable hands-on experience while catering to diverse learning styles, ensuring that students are actively involved in the material rather than merely consuming information. The integration of active learning strategies not only enhances student retention and comprehension but also cultivates a sense of autonomy as learners take ownership of their educational journey. Overall, embracing these approaches fosters a more engaging and enriching virtual learning experience for both educators and students alike.
2. Opportunities for Self-paced Mastery
In the realm of virtual learning, one of the greatest advantages is the opportunity for self-paced mastery. This approach allows learners to take control of their education, tailoring their study schedules to fit their individual needs and learning styles. In a traditional classroom setting, students are often forced to move at the pace of the majority, which can leave some feeling left behind or unchallenged. However, with self-paced mastery in virtual learning, individuals can delve deeper into subjects they find challenging or progress more quickly through material that comes easily to them.
Furthermore, self-paced mastery fosters independence and self-discipline in learners. With the freedom to manage their time and workload, students can develop important life skills such as time management and accountability. By setting their own goals and deadlines, individuals can learn how to structure their time efficiently and prioritize tasks—a crucial ability that will serve them well beyond academic endeavors. Additionally, this approach encourages a sense of ownership over one’s education, empowering learners to take charge of their intellectual growth and success.
C. Evaluation and Assessment
Virtual learning has brought about a new wave of evaluation and assessment methods, allowing for more personalized feedback and tailored learning experiences. With the use of advanced technologies, educators can track student progress in real-time, pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, and provide timely interventions to ensure academic success. Additionally, virtual assessment tools have the potential to incorporate multimedia elements such as videos, simulations, and interactive quizzes, catering to diverse learning styles and enhancing overall engagement.

However, one area of concern in virtual assessment is the potential for cheating or dishonesty due to the lack of physical supervision. Educators need to adapt their evaluation strategies to mitigate these risks while still fostering an environment conducive to honest self-assessment and academic integrity. Furthermore, there is an ongoing debate regarding the efficacy of standardized tests in a virtual learning environment, with proponents arguing for their continued relevance in measuring educational outcomes while critics point out their limitations in capturing holistic student performance.
1. Utilizing Technology for Comprehensive Assessments
With the advancement of technology, educators and trainers have been able to develop comprehensive assessment tools that provide a more accurate understanding of learners’ strengths and weaknesses. By utilizing online platforms, virtual simulations, and data analytics software, educators can assess various facets of learning such as critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and collaborative teamwork. These tools not only provide a holistic view of a student’s progress but also enable personalized feedback tailored to each individual’s needs.
Furthermore, technology allows assessments to be conducted in real-time, providing immediate insights into student performance. This instant feedback loop enables educators to make timely interventions and adjustments to their teaching strategies as needed. Additionally, digital assessments offer the flexibility for students to complete tasks at their own pace while still maintaining the rigor needed for effective evaluation. With this approach, technology has undeniably revolutionized the assessment process by offering more dynamic and interactive methods that cater to diverse learning styles.
2. Addressing Concerns of Academic Integrity
Addressing Concerns of Academic Integrity is a crucial aspect of virtual learning that cannot be overlooked. With the increasing use of online resources and distance communication, ensuring the authenticity and originality of students’ work has become a pressing issue. While technological tools like plagiarism checkers can help detect copied content, there’s also a need for proactive measures to promote academic honesty. Emphasizing proper citation methods, encouraging critical thinking, and designing varied assessment formats can all contribute to fostering an environment where academic integrity is valued.
Moreover, the shift to virtual learning has brought forth new challenges in maintaining fairness during examinations. Proctored online exams and remote invigilation systems have been introduced as solutions but may raise privacy concerns for students. Balancing the need for safeguarding exam integrity while respecting student privacy remains an ongoing debate in the virtual education sphere.
It’s evident that addressing concerns of academic integrity requires a multifaceted approach that considers the unique dynamics of virtual learning environments while upholding ethical standards.
V. Student Engagement and Motivation
Student engagement and motivation play a crucial role in the success of virtual learning. One of the key pros of virtual learning is the ability to tailor content and activities to cater to individual student interests and learning styles. This customization can significantly boost student engagement as they feel more connected to the material. Furthermore, incorporating interactive elements such as gamification or virtual group projects can enhance motivation by providing a sense of accomplishment and collaboration.
However, a potential con of virtual learning is the challenge of maintaining student engagement without physical interaction. Students may struggle with feelings of isolation or lack of motivation when studying independently. To address this, educators can emphasize regular communication and support networks to keep students engaged and motivated throughout their virtual learning journey. Additionally, leveraging technology like video conferencing for live discussions or guest speakers can provide valuable opportunities for students to stay connected and inspired by real-world experiences.
By prioritizing strategies that promote student engagement and motivation, educators can maximize the benefits while minimizing the drawbacks of virtual learning, ultimately enhancing the overall educational experience for students in a digital environment.
A. Gamification in Virtual Learning
Gamification in virtual learning has revolutionized the way students engage with educational content. By incorporating game elements such as challenges, rewards, and progress tracking into the virtual learning experience, educators can captivate students’ attention and motivate them to actively participate in their education. This approach not only makes learning more enjoyable but also fosters a sense of accomplishment and competitiveness among students, ultimately leading to improved retention of information and better overall performance.
Additionally, gamification provides a platform for collaborative learning where students can interact with each other in a fun and interactive manner. Through virtual games, simulations, and role-playing exercises, learners can apply theoretical knowledge to real-life scenarios, enhancing their critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities. Moreover, gamified virtual learning environments allow for personalized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs and preferences, thus promoting self-paced mastery of concepts while boosting confidence levels.
1. Incorporating Game Elements for Engagement
Incorporating game elements into virtual learning can significantly enhance engagement and motivation. By introducing elements such as point systems, leaderboard rankings, and achievement badges, educators can tap into the innate human desire for competition and reward. This creates a more dynamic and interactive learning environment that encourages active participation.
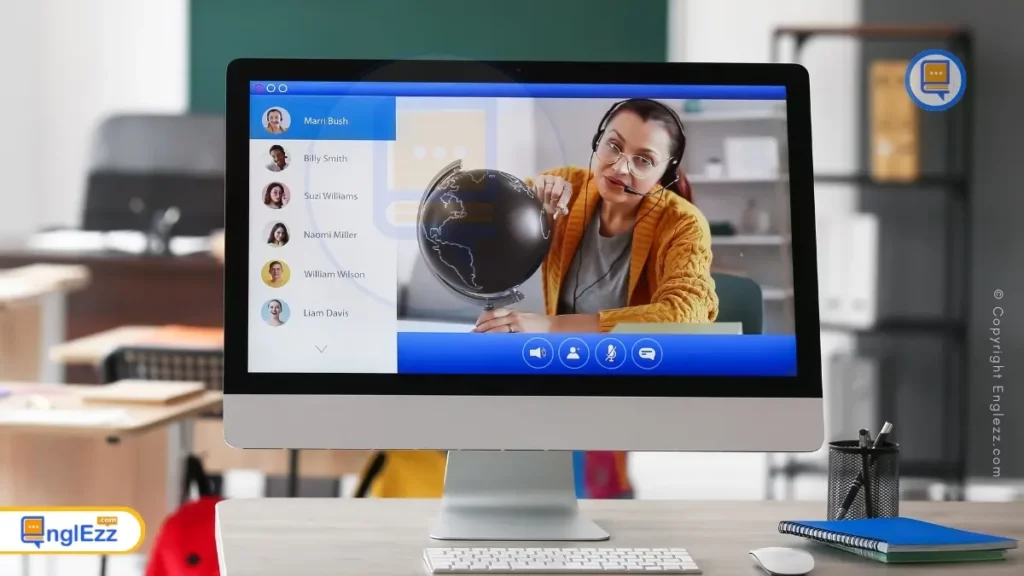
Furthermore, game elements can provide instant feedback to learners, allowing them to track their progress in real time. This not only fosters a sense of accomplishment but also helps identify areas for improvement. Additionally, incorporating storytelling and narrative elements into the learning experience can make complex concepts more relatable and memorable for students. Games have the potential to transform virtual learning from a passive activity into an immersive and participatory experience that keeps learners involved and eager to succeed.
2. Measuring Impact on Motivation Levels
Measuring impact on motivation levels is crucial in evaluating the effectiveness of virtual learning. One way to assess this impact is through regular feedback and surveys that gauge students’ engagement, interest, and overall motivation levels. Additionally, monitoring participation rates, completion of assignments, and active involvement in virtual discussions can provide valuable insights into the motivational aspects of virtual learning environments.
Furthermore, tracking changes in students’ performance over time can serve as a reflection of their level of motivation. By analyzing improvements or declines in academic achievement and comparing them to individual motivation levels, educators can gain a deeper understanding of how virtual learning influences students’ drive and commitment to their studies. These quantitative measures combined with qualitative data from student testimonials can offer a comprehensive view of the impact on motivation levels within the context of virtual learning.
B. Challenges in Sustaining Motivation
Sustaining motivation in a virtual learning environment comes with its fair share of challenges. One such obstacle is the lack of in-person interaction, which can make it difficult for students to stay engaged and motivated. Without the physical presence of teachers and classmates, it’s easy for some individuals to feel disconnected and less compelled to participate fully in their online studies.
Another challenge stems from the abundance of distractions that exist within one’s home environment. From social media notifications to household chores, staying focused on learning can prove to be quite demanding. This constant battle against distractions can lead to a decrease in motivation over time, making it essential for learners to develop effective strategies for maintaining their drive and concentration throughout their virtual learning journey.
1. Strategies for Maintaining Student Interest
When it comes to maintaining student interest in the virtual learning environment, incorporating interactive and engaging activities is crucial. Teachers can integrate platforms like Kahoot or Quizizz to make lessons more interactive and fun for students. Additionally, creating diverse learning experiences such as virtual field trips, live demonstrations, or guest speakers can also help keep students engaged and excited about learning.
Another effective strategy is to provide real-world applications of the material being taught. By demonstrating how the information relates to their lives or future careers, students are more likely to stay interested and motivated. Furthermore, encouraging peer collaboration through group discussions, projects, and presentations can foster a sense of community within the virtual classroom and pique student curiosity. Ultimately, maintaining student interest in virtual learning requires creativity, flexibility, and a keen understanding of what motivates and inspires each individual learner.
2. Addressing Virtual Fatigue
As virtual learning continues to be the norm for many, addressing virtual fatigue has become increasingly important. The constant screen time, lack of in-person interaction, and the blurring of personal and professional boundaries have all contributed to this sense of exhaustion. One approach to combatting virtual fatigue is to incorporate regular breaks into your schedule, allowing for moments of rest and rejuvenation away from the screen. Additionally, finding opportunities for offline social connections, such as outdoor activities or small group gatherings adhering to safety guidelines, can help alleviate the isolation that often accompanies virtual learning.
Furthermore, creating a dedicated workspace separate from leisure areas can provide a sense of routine and structure. This division helps establish clear boundaries between work or study time and relaxation periods. Practicing mindfulness techniques during short breaks can also aid in reducing mental fatigue and promoting focus during virtual sessions. By implementing these strategies and being aware of individual limits, it’s possible to mitigate the effects of virtual fatigue while maximizing the benefits of remote learning opportunities.
C. Student Participation and Interaction
Student participation and interaction in virtual learning environments have revolutionized the way students engage with their peers and educators. With the use of collaborative tools such as discussion forums, live chat sessions, and virtual group projects, students have more opportunities to interact with one another than ever before. This heightened level of interaction can lead to richer discussions, diverse perspectives, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
However, on the flip side, excessive reliance on virtual communication may also hinder meaningful interactions. Students may struggle to develop strong personal connections with their peers and instructors. As a result, it’s essential for educators to find a balance between leveraging technology for increased student participation and ensuring that meaningful human connections are still prioritized.
In conclusion, while virtual learning has opened up new avenues for student participation and interaction, it’s crucial for educators to be mindful of its potential drawbacks in order to foster a truly enriching learning experience for all participants.
1. Encouraging Active Participation in Virtual Discussions
Encouraging active participation in virtual discussions is crucial for creating a dynamic and engaging online learning environment. One effective strategy is to set clear expectations for participation from the outset, encouraging students to contribute regularly through comments, questions, or even leading discussions on specific topics. By promoting an inclusive and respectful atmosphere, where all voices are valued, instructors can motivate students to actively engage in virtual discussions.
Furthermore, incorporating interactive elements such as polls, breakout room activities, and collaborative projects can inject life into virtual discussions. These immersive experiences not only foster a sense of community but also provide opportunities for deeper critical thinking and problem-solving skills development. Additionally, leveraging multimedia resources such as videos or podcasts can enrich the discussion experience and capture the attention of participants effectively. Ultimately, by implementing these strategies, educators can stimulate active engagement in virtual discussions while enhancing the overall quality of the online learning experience.
2. Balancing Individual and Collaborative Tasks
Balancing individual and collaborative tasks is a crucial skill in the virtual learning environment. While individual tasks allow students to develop their independent thinking and problem-solving abilities, collaborative tasks enable them to hone their teamwork and communication skills. Striking a balance between these two types of activities can help students build a well-rounded set of competencies, preparing them for the demands of the modern workforce.
It’s important for virtual learners to recognize when it’s beneficial to work on their own and when they should seek input from peers. Over-reliance on one mode over the other can limit growth opportunities. Encouraging students to find this equilibrium can lead to greater academic success while nurturing essential life skills necessary for thriving in today’s interconnected world.
VI. Impact on Traditional Educational Models
The impact of virtual learning on traditional educational models cannot be understated. While some critics argue that virtual learning diminishes the face-to-face interaction essential in traditional education, others argue that it offers a more flexible and personalized approach for students. One undeniable impact is the democratization of education, as virtual learning breaks down geographical barriers and provides access to high-quality education for individuals who may not have had the opportunity otherwise.
Moreover, virtual learning also challenges the traditional lecture-based model by encouraging a more interactive and collaborative approach to education. It allows for innovative teaching methods using multimedia tools, simulations, and online platforms, engaging students in ways that were previously impossible in a traditional classroom setting. However, it’s important to address potential drawbacks such as screen fatigue and decreased social interactions for students engaged in prolonged periods of virtual learning.
A. Shift in Pedagogical Paradigms
The shift in pedagogical paradigms towards more student-centered and interactive learning approaches has been a positive outcome of the virtual learning revolution. Traditional teacher-centric education systems have given way to collaborative and inquiry-based methodologies, where students are empowered to take charge of their own learning. This shift has encouraged critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and creativity, fostering a more holistic development of students.
Furthermore, virtual platforms have expanded educational access, allowing for global collaboration and the exchange of diverse perspectives among students from different cultural backgrounds.
As pedagogical paradigms continue to evolve in the realm of virtual learning, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. One such concern is the potential for increased student isolation due to the lack of physical interaction in virtual classrooms. The absence of non-verbal cues in digital communication can also hinder effective teacher-student relationships.
Additionally, maintaining student engagement and motivation over extended periods of screen-based learning requires innovative teaching strategies that cater to diverse learning styles. Balancing these pros and cons is essential for harnessing the full potential of virtual learning while addressing its limitations.
1. Redefining the Role of Instructors
In this digital age, the role of instructors is undergoing a fundamental shift. No longer are they simply disseminators of information; instead, they are facilitators of learning and cultivators of critical thinking skills. In the virtual learning environment, instructors must adapt to become mentors who inspire curiosity, guide students in navigating vast amounts of information, and foster collaborative problem-solving. By redefining their role as facilitators rather than lecturers, instructors can create a more engaging and interactive learning experience for their students.
Furthermore, with the increasing prevalence of online education, instructors have an unprecedented opportunity to personalize their approach to meet individual student needs. They can leverage technology to tailor content delivery and assessment methods while providing timely feedback and support. By embracing this new role as personalized learning advocates, educators can empower students to take ownership of their learning journey and develop lasting skills beyond mere rote memorization. It’s a transformative era for instructors where creativity meets technology in reshaping the dynamics of education delivery.
2. Student-Centric Approaches in Virtual Environments
In the realm of virtual learning, student-centric approaches have emerged as a guiding principle for creating meaningful and effective educational experiences. By placing students at the center of the learning process, virtual environments can be tailored to meet individual needs and preferences. One significant aspect of student-centric approaches is the ability to offer personalized feedback and support in real-time, allowing for immediate intervention and guidance when students encounter challenges. This focus on individualized learning promotes a sense of ownership and empowerment among students, fostering a strong sense of responsibility for their own progress.
Another key benefit of student-centric approaches in virtual environments is the opportunity for increased collaboration and social interaction among peers. With the use of digital platforms, students can engage in group projects, discussions, and cooperative activities that encourage active participation and shared knowledge building.
This not only enhances social connectivity but also simulates real-world interactions, preparing students for future professional endeavors where teamwork and communication skills are essential. Overall, embracing student-centric approaches in virtual learning environments not only prioritizes personal growth but also cultivates a supportive community conducive to holistic development.
B. Hybrid Learning Models
Hybrid learning models, a blend of in-person and virtual instruction, have revolutionized the education landscape. Such an approach offers students the benefits of face-to-face interaction while leveraging technology for flexibility and personalized learning. This model also enhances students’ digital literacy and self-discipline, crucial skills in today’s fast-paced world. Moreover, it allows for seamless adaptation to various circumstances such as weather disruptions or health-related issues.
Embracing hybrid learning models can lead to unique challenges, such as potential disparities in access to technology and resources among students. Additionally, educators are required to develop diverse teaching methods that cater to both in-person and online learners simultaneously, necessitating extra preparation time. While this may initially pose logistical hurdles, mastering the art of hybrid learning has the potential to create a more adaptable and inclusive educational environment where all students can thrive.
In conclusion, embracing hybrid learning models with open-mindedness paves the way for a truly modern education system that caters to diverse student needs effectively. It is essential that institutions provide comprehensive support and resources for both educators and students alike during this transitional period towards adopting new modes of learning.
1. Integrating Virtual and Physical Learning Spaces
Integrating virtual and physical learning spaces offers a wealth of opportunities for students to acquire knowledge in diverse ways. By combining these two platforms, educators can create a dynamic learning environment that caters to different learning styles and preferences. Physical spaces can facilitate hands-on activities, group discussions, and immediate teacher-student interactions, while virtual spaces can provide access to a vast array of digital resources, online collaboration tools, and interactive multimedia content. This integration enables students to experience the best of both worlds – fostering creativity, critical thinking skills, and adaptability essential for their future endeavors.
Moreover, blending virtual and physical learning spaces promotes inclusivity by accommodating the needs of all students regardless of their geographical location or physical abilities. It allows educators to leverage technology to reach remote learners who may not have easy access to traditional classrooms. Additionally, this integration encourages the utilization of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies that bring abstract concepts to life while bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications.
With advancements in technology continuing to blur the lines between virtual and physical realms, educators have an unprecedented opportunity to craft personalized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs while preparing them for an increasingly digital world.
2. Adapting Curriculum to Hybrid Models
As schools continue to navigate the challenges of virtual and hybrid learning models, adapting curriculum has become a crucial aspect of ensuring students receive a comprehensive education. One approach involves incorporating multimedia content and interactive resources to create engaging online lessons that cater to varying learning styles.
By leveraging digital tools, educators can personalize instruction and provide dynamic experiences that transcend the limitations of traditional classroom settings. Furthermore, adjusting curriculum to reflect real-world applications and current events enables students to develop critical thinking skills and stay connected with global issues.

Another aspect of adapting curriculum to hybrid models involves maintaining a balance between synchronous and asynchronous learning experiences. This approach allows students the flexibility to engage in self-paced activities while also participating in live discussions and collaborative projects. By carefully integrating these components into the curriculum, educators can promote independence, creativity, and effective time management skills among their students.
Additionally, providing access to well-organized digital content ensures continuity in learning regardless of the setting, thus equipping students with essential skills for success in both academic pursuits and future careers.
C. Challenges in Institutional Transition
Institutional transition, especially in the context of shifting from traditional classroom-based learning to virtual education, presents a myriad of challenges that institutions must navigate. One of the main hurdles is the need for significant technological infrastructure and support systems to ensure a seamless transition. This means not only investing in appropriate hardware and software but also ensuring educators and students are proficient in using these tools effectively. Additionally, there is a crucial need to address disparities in digital access among students, as some may not have equal access to internet connectivity or devices required for virtual learning.
Another major challenge that arises during institutional transition is the potential resistance or hesitation from both educators and students towards adapting to new modes of learning. Educators may struggle with redesigning their teaching methods to suit online platforms, while students might find it challenging to stay focused and engaged without the physical presence of their peers and instructors. Overcoming these challenges requires proactive measures such as targeted training for educators on online teaching techniques, as well as creating interactive and collaborative virtual environments that mimic traditional classroom interactions.
The complexities involved in managing institutional transition demand strategic planning and proactive problem-solving from educational leadership. It’s crucial for institutions embarking on this journey to anticipate these challenges and implement comprehensive solutions that foster a smooth shift towards virtual learning while prioritizing equitable access and effective pedagogy.
1. Faculty Training and Development
Faculty training and development is a critical component of successful virtual learning. With the rapid advancement of technology and online teaching methods, faculty members need continuous training to adapt to new tools and platforms. This not only enhances their teaching skills but also keeps them updated with the latest instructional techniques. Furthermore, professional development opportunities for faculty can lead to improved student engagement and performance, as educators gain insights into using digital resources effectively.
However, one challenge in faculty training for virtual learning is ensuring that all instructors receive equitable access to resources and support. Disparities in technological literacy among faculty members can impact the effectiveness of virtual teaching. To address this issue, institutions must provide comprehensive training programs tailored to individual needs, offering ongoing assistance to ensure that each instructor feels confident in utilizing online tools.
Overall, investing in faculty training and development is crucial for enhancing the quality of virtual education while empowering educators with the necessary skills and knowledge for effective online instruction.
2. Infrastructural Investments and Considerations
Infrastructural investments play a crucial role in shaping the success of virtual learning initiatives. From robust internet connectivity to reliable hardware and software, educational institutions must consider a wide range of factors when making these investments. One important consideration is the digital divide, which highlights disparities in access to technology and high-speed internet among students. Addressing this gap not only requires financial commitments but also strategic planning to ensure equitable access for all learners.
Furthermore, infrastructural investments can impact the quality of virtual learning experiences. Investing in state-of-the-art learning management systems, interactive platforms, and virtual collaboration tools can enrich the educational environment and foster greater student engagement. However, striking a balance between cutting-edge technologies and user-friendly interfaces is vital to ensure that infrastructure investments align with educators’ pedagogical goals without overwhelming learners with complex systems. As such, thoughtful consideration of infrastructural needs is essential for creating seamless and inclusive virtual learning environments that benefit both students and educators.
VII. Future Trends in Virtual Learning
As we look ahead to the future of virtual learning, several trends are poised to reshape the landscape of education. One key trend is the advancement of virtual reality (VR) technology, which has the potential to create immersive and interactive educational experiences. By utilizing VR, students can engage in realistic simulations and experiential learning activities that transcend the limitations of traditional classroom settings. Additionally, personalized learning pathways driven by artificial intelligence are expected to become more prevalent in virtual learning environments. This approach allows for tailored instruction based on individual student needs and preferences, ultimately enhancing student engagement and academic success.
Furthermore, as technology continues to evolve, augmented reality (AR) is anticipated to play a significant role in virtual learning by integrating digital information into real-world environments. This will enable students to interact with digital content within their physical surroundings, fostering a deeper understanding of complex concepts. Another emerging trend is the emphasis on collaborative online learning communities, where students can collaborate across geographic boundaries and cultural differences. These communities promote global citizenship and provide opportunities for diverse perspectives and knowledge sharing essential for today’s interconnected world.
A. Advancements in Virtual Reality
Advancements in Virtual Reality have completely transformed the landscape of learning, offering an immersive experience that goes beyond traditional methods. With the development of more realistic graphics and motion tracking devices, VR has become increasingly interactive, allowing users to engage with their virtual environments in a truly hands-on way. Furthermore, advancements in haptic feedback technology have added a new dimension to VR experiences, enabling users to physically feel and interact with virtual objects, enhancing the overall learning experience.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into Virtual Reality platforms has vastly improved user experiences by creating personalized and adaptive content. This not only enhances engagement but also ensures that learners receive tailored content based on their individual needs and progress. Advancements in wearables such as VR headsets have also made these experiences more accessible than ever before, bringing high-quality immersive learning to a wider audience. As these technologies continue to advance, the future holds even more promising possibilities for how VR can revolutionize education and training.
1. Immersive Learning Experiences
Immersive learning experiences have quickly gained traction as a powerful tool in the world of education. By leveraging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), students can step into simulated environments that simulate real-world scenarios, greatly enhancing their understanding and retention of complex concepts. For example, medical students can practice surgeries in a VR environment or history students can virtually visit ancient civilizations, bringing textbooks to life. This hands-on approach not only makes learning more engaging but also fosters a deeper level of understanding.
Moreover, immersive learning experiences offer unparalleled levels of accessibility and inclusivity. Students with physical disabilities or those living in remote areas can access the same high-quality educational experiences as their peers through virtual platforms. This promotes diversity and equity in education as it eliminates traditional barriers to learning. Additionally, these innovative tools cater to various learning styles, accommodating visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners alike. The ability to tailor the learning experience to individual needs is a significant advantage of immersive technologies in education.
2. Practical Applications in STEM Education
STEM education, with its focus on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, opens numerous doors for practical applications that can benefit both students and society as a whole. By integrating real-world problems into the curriculum, educators can encourage critical thinking and problem-solving skills in their students. For example, using robotics to solve everyday challenges or exploring renewable energy sources through hands-on experiments can give students a tangible understanding of theoretical concepts. This not only increases engagement but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relevance of STEM subjects in their lives.
Furthermore, practical applications in STEM education provide valuable opportunities for interdisciplinary learning. Students can bring together knowledge from various fields to address complex issues such as climate change or healthcare innovation. By working on cross-disciplinary projects, they develop teamwork and communication skills while gaining insight into how different scientific principles intersect and interact. This holistic approach enhances their ability to tackle multifaceted problems in an increasingly interconnected world.
B. Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing personalized learning by providing tailored education experiences to individual students. Through AI-powered platforms, students can receive customized content and support based on their unique learning styles, preferences, and abilities. This allows for a more effective and engaging learning experience, as the material presented is specifically targeted to each student’s needs.
Moreover, AI in personalized learning can also help identify gaps in a student’s understanding and offer additional resources or guidance to address those areas. By analyzing a student’s performance data and behavior patterns, AI can provide valuable insights to educators about the individualized needs of each student. This ability to adapt instruction based on real-time feedback can significantly enhance the effectiveness of virtual learning environments.
Furthermore, AI fosters collaborative learning opportunities by facilitating peer-to-peer interactions and group projects tailored to students’ strengths and weaknesses. With AI technology continuously analyzing student progress and adapting instruction accordingly, virtual learning becomes more responsive and effective at meeting the diverse needs of individual learners.
1. Adaptive Learning Algorithms
Adaptive learning algorithms have revolutionized the virtual learning experience by personalizing education to individual students. By constantly analyzing student performance and adjusting the content and pace accordingly, these algorithms ensure that each learner receives a customized learning path tailored to their strengths and weaknesses. This approach not only fosters a deeper understanding of the material but also enhances student motivation by providing a sense of autonomy and control over their learning journey.
Moreover, adaptive learning algorithms can effectively cater to diverse learner needs, accommodating different paces of comprehension and varying levels of prior knowledge. This adaptability is especially beneficial in virtual learning environments where students come from various backgrounds and may require more flexibility in their educational experiences. Additionally, these algorithms contribute to a more efficient use of time by targeting specific areas for improvement, ultimately promoting better academic outcomes while allowing educators to focus on other essential aspects of teaching.
2. Virtual Learning Assistants
Virtual Learning Assistants have revolutionized the way students interact with educational content. These AI-powered tools provide personalized support, instant feedback, and adaptive learning experiences tailored to individual needs. Imagine a virtual assistant that can guide a student through complex problem-solving exercises, monitor their progress in real-time, and suggest additional resources for further improvement. This level of personalized assistance not only enhances the learning process but also empowers students to take ownership of their education.
Furthermore, Virtual Learning Assistants are available 24/7, breaking free from the constraints of traditional classroom hours. Students can access support whenever they need it, fostering a culture of continuous learning and self-improvement. This accessibility also extends to students with diverse learning styles or special educational needs, ensuring that no one is left behind in the pursuit of knowledge. As technology continues to advance, these Virtual Learning Assistants will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of education by providing tailored support and guidance to learners worldwide.
C. Global Collaborations in Virtual Spaces
In today’s interconnected world, the concept of global collaborations in virtual spaces has rapidly transformed how individuals and organizations interact. The ability to connect with people from different countries and cultures in real time has expanded opportunities for cross-cultural learning and collaboration. Through virtual platforms, individuals can engage in projects, discussions, and activities with counterparts from around the globe, fostering a sense of international community and understanding.
One significant advantage of global collaborations in virtual spaces is the potential for diverse perspectives to enrich problem-solving processes. By bringing together individuals with varying backgrounds and experiences, virtual collaboration can lead to innovative solutions that may not have been possible within a homogenous group. Additionally, the accessibility of virtual platforms enables widespread participation, breaking down geographical barriers and facilitating meaningful exchanges among individuals who would otherwise be unable to connect physically.
Moreover, global collaborations in virtual spaces offer immense potential for professional networking and skill development. As individuals engage in joint initiatives with global partners, they gain exposure to different work cultures and practices while honing their communication skills across linguistic and cultural boundaries. This exposure not only broadens individual horizons but also cultivates an environment where new ideas flourish through shared insights from diverse participants.
Overall, these advancements demonstrate how global collaborations in virtual spaces are paving the way for more inclusive forms of learning and interaction by leveraging technology to bridge geographical divides.
1. International Classroom Experiences
International classroom experiences offer students a unique opportunity to broaden their cultural horizons and gain a global perspective on various subjects. Through interacting with classmates from different countries, students can gain valuable insights into diverse perspectives, traditions, and customs. This exposure fosters open-mindedness and enhances critical thinking as students are encouraged to consider alternative viewpoints and approaches to problem-solving. Moreover, these international interactions often lead to friendships that transcend geographical borders, creating a network of contacts that could prove invaluable in future endeavors.
However, it’s essential to recognize the challenges that come with international classroom experiences. Language barriers, time zone differences, and varying academic expectations can pose significant hurdles for effective collaboration. Additionally, cultural misunderstandings may arise, requiring sensitivity and open communication to address. Nevertheless, these challenges provide invaluable learning opportunities related to cross-cultural communication and adaptability – essential skills for today’s interconnected world. Ultimately, the international classroom experience offers immense value by preparing students for global citizenship and providing them with a competitive edge in an increasingly multicultural workforce.
2. Cultural Diversity in Virtual Learning Communities
The cultural diversity present in virtual learning communities adds a rich and dynamic element to the online educational experience. Students from different backgrounds bring unique perspectives, experiences, and knowledge to the virtual classroom, creating a vibrant tapestry of ideas and insights. This diversity fosters a more inclusive environment where students can learn from each other’s varying cultural viewpoints, breaking down barriers and enriching their understanding of global issues.
Furthermore, exposure to diverse cultures in virtual learning communities promotes empathy, tolerance, and cross-cultural communication skills. As students interact with peers from different ethnicities, languages, and traditions, they are exposed to new ways of thinking and problem-solving. This not only enhances their academic learning but also prepares them for the multicultural dynamics of today’s global workforce. Embracing cultural diversity in virtual learning communities is essential for nurturing well-rounded individuals who can thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
VIII. Legal and Ethical Considerations:
As virtual learning continues to expand, it brings to the forefront several legal and ethical considerations. Privacy concerns regarding student data protection and online security have become increasingly relevant. Institutions must ensure compliance with regulations such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) to safeguard student information. Additionally, educators face ethical dilemmas related to maintaining academic integrity in virtual classrooms, with concerns about cheating, plagiarism, and unauthorized assistance being more challenging to address in an online environment.
Moreover, access and equity issues arise when considering virtual learning, as not all students have equal access to necessary technology or a conducive learning environment at home. This presents a legal and ethical challenge for educational institutions striving to provide fair opportunities for all students. Balancing the benefits of virtual learning with these legal and ethical complexities requires thoughtful consideration and proactive measures from both educators and policymakers alike.
A. Data Privacy and Security
In the age of virtual learning, data privacy and security have become paramount concerns for both educational institutions and students. While the convenience of online education is undeniable, it also opens up a Pandora’s box of potential vulnerabilities. From the collection and storage of personal information to the risk of cyberattacks, ensuring robust data privacy measures is essential.
One pro of virtual learning in relation to data privacy is the potential for enhanced control over personal data. With the right tools and policies in place, educational platforms can empower students to manage their own information more effectively, giving them greater autonomy and transparency. However, a significant con is the increased susceptibility to cyber threats due to the vast amounts of sensitive data being transmitted electronically. This necessitates a heightened focus on implementing strong encryption protocols and regular security audits to protect against potential breaches.
Ultimately, embracing virtual learning requires a delicate balance between leveraging technology for educational advancement while safeguarding sensitive information from potential risks. This duality underscores the critical importance of continuously evolving data privacy standards within the realm of online education.
1. Ensuring Confidentiality of Student Information
In today’s digital age, the protection of student information is of paramount importance. Virtual learning platforms necessitate the collection and storage of vast amounts of sensitive data, prompting a heightened need for robust confidentiality measures. Implementing encryption protocols and secure access controls can help safeguard this information from unauthorized access or breaches. However, striking a balance between accessibility for educators and maintaining confidentiality poses a significant challenge in the virtual realm.
Furthermore, the increased reliance on third-party service providers in virtual learning introduces additional complexities to ensuring student data confidentiality. Institutions must meticulously vet these vendors to ensure their compliance with rigorous data protection standards and regulations. Additionally, educating both staff and students about best practices for handling sensitive information can empower them to actively contribute to maintaining confidentiality within the virtual learning environment. Ultimately, prioritizing student information privacy not only fosters trust but also upholds ethical responsibilities in an ever-evolving educational landscape.
2. Complying with Data Protection Regulations
Complying with data protection regulations is an essential aspect of virtual learning. While digital platforms offer convenience and accessibility, they also raise concerns about the security and privacy of data. Adhering to regulations such as the GDPR and COPPA ensures that students’ personal information is safeguarded, fostering a safe online environment for learning.
Furthermore, compliance with data protection regulations builds trust between educational institutions and students and their parents. By demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information, schools can alleviate concerns about potential data breaches or misuse of personal data. Additionally, adherence to these regulations fosters responsible digital citizenship among students, imparting valuable lessons on privacy rights in the digital age. Overall, while compliance may pose initial challenges, the benefits of prioritizing data protection far outweigh the drawbacks in virtual learning environments.
B. Equity in Access to Virtual Learning
Equity in Access to Virtual Learning is a crucial aspect that demands attention in the current educational landscape. While virtual learning has opened up opportunities for students who may not have otherwise had access to education, it has also brought to light the stark inequities that exist in terms of technology and internet access. Students from low-income households or rural areas often lack the necessary devices and reliable internet connections, placing them at a significant disadvantage compared to their more privileged counterparts. This disparity raises important questions about how virtual learning can be made accessible to all students, regardless of their socio-economic backgrounds.
In addressing equity in access to virtual learning, solutions must go beyond simply providing hardware and internet connectivity. Understanding the unique challenges faced by different communities is essential for developing effective strategies. For instance, initiatives that involve partnering with local community centers or libraries to provide study spaces and access to resources may prove beneficial for students lacking home resources. Additionally, advocating for policies that prioritize equitable distribution of technology and broadband access is imperative at both local and national levels. By approaching equity in virtual learning holistically, we can work towards ensuring that every student has an equal opportunity to thrive in the digital educational environment.
1. Bridging Socioeconomic Gaps
Bridging socioeconomic gaps is one of the most crucial challenges in the education system, and virtual learning has the potential to address this issue. By providing equal access to educational resources and opportunities, virtual learning can help level the playing field for students from different socioeconomic backgrounds. For example, students from low-income families may have better access to online educational materials and courses that they otherwise wouldn’t have access to in a traditional classroom setting. Additionally, virtual learning can provide flexibility for students who may need to work part-time or care for family members, allowing them to continue their education without sacrificing other responsibilities.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that not all students have equal access to digital devices and high-speed internet connections. This presents a significant obstacle for bridging socioeconomic gaps through virtual learning. Without addressing these accessibility issues, there is a risk of widening the gap between affluent students with easy access to technology and less privileged students who struggle with digital divide. Moreover, some educators argue that virtual learning can perpetuate existing inequalities by assuming all students have equal support structures at home.
In conclusion, while virtual learning holds promise in bridging socioeconomic gaps by offering broader educational opportunities, it’s essential to address technological disparities and ensure equitable access for all learners.
2. Legal Implications of Unequal Access
The unequal access to virtual learning platforms raises significant legal implications that cannot be overlooked. The disparity in access to technology and internet connectivity among students may lead to potential cases of discrimination and violation of equal educational opportunities. Schools and educational institutions must navigate the complexities of providing equitable access as mandated by federal laws such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Title VI of the Civil Rights Act, which prohibit discrimination based on race, color, or national origin. Failure to address these disparities could result in legal challenges that have far-reaching implications for educational institutions.
Furthermore, the digital divide exacerbates existing socioeconomic disparities, potentially leading to legal challenges related to the infringement of students’ rights to a fair and inclusive education. Legal experts are grappling with how best to address these issues within the framework of existing laws while also championing for new legislation that specifically addresses digital equity in education.
As virtual learning becomes increasingly integral to modern education, it is imperative that legislators and policymakers urgently tackle these legal ramifications to ensure all students have equal opportunities for success.
C. Academic Integrity in Virtual Assessments
Academic integrity in virtual assessments is a critical aspect of the evolving landscape of remote education. The transition to virtual learning has prompted an urgent need to ensure that students maintain ethical standards when completing assessments online. With the absence of direct supervision, there’s an increased risk of cheating and academic dishonesty. It’s essential for educators to explore innovative methods for ensuring academic integrity, such as using plagiarism detection software and designing assessments that emphasize critical thinking and application rather than rote memorization.

Furthermore, virtual assessments offer new opportunities for authentic evaluation methods that can better reflect real-world skills. For instance, project-based assessments and open-book exams can encourage deeper engagement with the material while reducing the likelihood of cheating.
Educators should leverage technology to create interactive and dynamic assessment experiences, fostering a culture of integrity in virtual learning environments. Ultimately, promoting academic integrity in virtual assessments involves a combination of technological solutions and pedagogical approaches aimed at inspiring genuine intellectual growth in students.
1. Implementing Effective Anti-plagiarism Measures
Implementing effective anti-plagiarism measures is essential in the virtual learning environment to uphold academic integrity and foster original thinking. One of the most impactful strategies is the use of advanced plagiarism detection software, which not only identifies matching content but also analyzes contextual information to provide a clearer picture of potential plagiarism. Furthermore, promoting a culture of citation and attribution can encourage students to acknowledge their sources and take ownership of their work.
Another key approach is to incorporate project-based assessments that require critical thinking and creativity, making it more arduous for students to simply copy and paste material from the internet. Additionally, providing clear guidelines on proper paraphrasing and citing sources can equip students with the necessary skills to avoid accidental plagiarism, thereby promoting a deeper understanding of academic honesty. By implementing these measures, educators can cultivate an environment where originality is celebrated and upheld as an integral aspect of learning in virtual settings.
2. Addressing Challenges in Remote Proctoring
In the realm of virtual learning, remote proctoring has emerged as both a solution and a challenge. While it offers the convenience of conducting exams from anywhere, ensuring its integrity and fairness can be daunting. One primary concern revolves around privacy invasion and data security. The use of webcams to monitor students during exams raises valid fears about potential breaches in personal privacy. Additionally, there’s also the risk of technical glitches disrupting the exam process, leading to unwarranted stress for both students and exam administrators.
Beyond these concerns, another challenge lies in striking a balance between security measures and accessibility for all students. Implementing stringent proctoring mechanisms may inadvertently disadvantage individuals with limited access to stable internet connections or high-quality webcams. On top of that, it’s crucial to consider how remote proctoring might introduce biases based on cultural differences or socio-economic factors present in various regions. These challenges underscore the need for innovative approaches that prioritize fairness while navigating the intricacies of remote proctoring in virtual learning environments.
IX. Recommendations for Successful Virtual Learning Implementation
- Embrace Innovative Teaching Methods – Successful virtual learning implementation requires educators to embrace innovative teaching methods that engage students in a dynamic and interactive way. Incorporating multimedia tools, gamified learning experiences, and real-time collaboration platforms can create an enriching virtual classroom environment that stimulates active participation and deep understanding.
- Prioritize Personalized Support – To ensure the success of virtual learning, it is crucial for educational institutions to prioritize personalized support for students. This includes providing access to individualized tutoring, counseling services, and technical assistance to address any challenges or barriers that students may encounter while navigating the online learning environment.
- Foster a Strong Sense of Community – Building a strong sense of community within the virtual classroom is essential for successful implementation of virtual learning. Educators should facilitate regular group discussions, collaborative projects, and peer-to-peer interactions to foster a supportive and inclusive learning environment where students feel connected and motivated to excel in their academic pursuits.
A. Faculty Training Programs
Faculty training programs have become a vital component of the transition to virtual learning. These programs equip educators with the digital competencies needed to deliver effective online instruction, emphasizing innovative teaching methodologies and technological proficiency. One key advantage is that faculty training programs foster a community of practice among educators, allowing them to collaborate, share best practices, and collectively address common challenges in virtual learning environments.
Moreover, these programs can empower faculty members by providing them with the tools and knowledge necessary to adapt their teaching styles and engage students in meaningful ways within the online realm.
On the flip side, some criticisms of faculty training programs focus on potential time constraints and resource limitations. Faculty may find it challenging to balance teaching responsibilities with professional development through these programs. Additionally, concerns about the effectiveness of training methods delivered virtually rather than through traditional face-to-face interactions might arise. However, ongoing evaluation and adaptation of these training programs can help mitigate such drawbacks and ensure that faculty receive adequate support during this educational evolution.
1. Technological Proficiency
Technological proficiency in the context of virtual learning is a crucial skill that goes beyond merely using digital tools. It encompasses the ability to navigate various platforms, troubleshoot technical issues, and harness technology for effective communication and collaboration. Students with strong technological proficiency not only excel in their academic pursuits but also develop crucial skills for the modern workforce where digital literacy is paramount.
Furthermore, mastering technology enables students to access a wealth of resources and information, fostering independent learning and critical thinking. With technological proficiency, learners can leverage multimedia resources, online databases, and interactive simulations to deepen their understanding of complex concepts. However, it’s important to note that technological proficiency should be complemented by responsible digital citizenship to ensure ethical use of online resources and respectful communication in virtual learning environments.
2. Pedagogical Strategies for Virtual Environments
In the realm of virtual learning, pedagogical strategies play a crucial role in shaping the educational experience for students. One effective approach is the implementation of interactive simulations and virtual labs, which provide hands-on learning experiences that mirror real-world scenarios. This not only engages students on a deeper level but also fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Additionally, incorporating collaborative projects within virtual environments allows for peer interaction and teamwork, mirroring the dynamics of an in-person classroom.
Furthermore, personalized learning pathways can be easily facilitated in virtual environments through adaptive software and AI-powered tools. These tailored pathways cater to individual student needs and pace, ensuring that each learner receives a customized educational experience. By leveraging these pedagogical strategies effectively, educators can create rich and immersive virtual classrooms that empower students to thrive in digital learning landscapes.
B. Robust Technical Support Systems
As virtual learning becomes more prevalent, the need for robust technical support systems has never been higher. These systems play a vital role in ensuring that students and educators have seamless access to the necessary tools and resources. From troubleshooting technical issues to providing timely guidance, a strong support system can minimize disruptions and maximize the learning experience.
One of the key advantages of robust technical support systems is their ability to address diverse technological challenges. Whether it’s navigating unfamiliar software or resolving connectivity issues, proficient support teams can offer tailored solutions to meet individual needs. Additionally, these systems empower users by providing them with the knowledge and skills needed to overcome similar obstacles in the future, fostering a sense of independence and confidence in using digital platforms for education.
1. Quick Resolution of Technical Issues
In the realm of virtual learning, one undeniable advantage is the quick resolution of technical issues. With the ability to troubleshoot problems remotely, students and instructors can swiftly address any technological hiccups that may arise during online classes. Whether it’s a glitchy video call or a malfunctioning software, the prompt intervention of IT support or tech-savvy individuals ensures minimal disruption to the learning process.
Furthermore, the seamless integration of cloud-based platforms and digital tools allows for efficient problem-solving. Instead of waiting for on-site technicians or scheduling in-person appointments, virtual learners benefit from rapid solutions that enhance their overall academic experience. This streamlined approach not only fosters productivity but also promotes adaptability and resilience in navigating digital challenges – vital skills in today’s technology-driven world.
2. User-Friendly Troubleshooting Resources
User-friendly troubleshooting resources are a crucial aspect of virtual learning, as technical issues can hinder the educational experience. Fortunately, there is a myriad of easily accessible resources available for students and educators alike. Online forums and communities provide a wealth of troubleshooting advice, with fellow users often sharing their experiences and solutions to common problems. Additionally, many educational platforms offer comprehensive knowledge bases and video tutorials that guide users through resolving technical issues efficiently.
The beauty of user-friendly troubleshooting resources lies in their ability to empower individuals to tackle challenges independently. By having access to comprehensive guides and support documentation, students and educators can quickly address technical setbacks without relying on external assistance. This not only promotes self-reliance but also fosters a sense of accomplishment when successfully resolving issues. However, it’s essential for institutions to ensure these resources are up-to-date and easily navigable, allowing users to find solutions without unnecessary frustration or wasted time.
C. Continuous Feedback and Improvement
Continuous feedback and improvement are crucial aspects of virtual learning that can significantly enhance the educational experience. By providing students with frequent, specific feedback on their performance, educators can help them identify areas for growth and development. This ongoing dialogue not only fosters a sense of collaboration but also empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey. Moreover, the ability to adapt and improve in real time allows virtual learning to be more responsive to individual student needs.
However, despite the numerous advantages, continuous feedback and improvement in virtual learning also present challenges. The constant stream of information can be overwhelming for both educators and students, potentially leading to burnout or disengagement. Additionally, ensuring the quality and consistency of feedback across various online platforms can be a daunting task. Striking a balance between providing enough feedback for progress while avoiding information overload is essential for maximizing the benefits of continuous improvement in virtual learning.
1. Gathering Student Feedback on Virtual Learning Experience
In the age of virtual learning, gathering student feedback has become pivotal in understanding their experiences and addressing potential shortcomings. One effective way to obtain such insight is through anonymous surveys that allow students to express their thoughts openly without fear of repercussions. Additionally, conducting focus groups or individual interviews can provide nuanced feedback on specific aspects of the virtual learning experience, giving educators a comprehensive understanding of what works and what needs improvement.
Moreover, incorporating real-time feedback mechanisms during online classes can offer immediate insights into student engagement and comprehension. Technologies like polling tools or chat functions not only enable educators to gauge student sentiments but also create an interactive environment that fosters open communication. In this way, gathering continuous feedback becomes a collaborative effort between students and teachers, allowing for agile adjustments in virtual learning strategies based on real-time input.
2. Iterative Improvements to Virtual Learning Platform
One of the most fascinating aspects of virtual learning platforms is the continuous iterative improvements that are fueling their evolution. The dynamic nature of technology allows for ongoing enhancements to user interface design, interactive features, and overall performance. As we witness this constant refinement, it’s clear that virtual learning platforms are not static entities but rather adaptive systems that respond to user feedback and technological advancements.
Additionally, iterative improvements contribute to the customization and personalization possibilities within virtual learning environments. Features such as adaptive learning algorithms, personalized recommendations, and tailored assessment tools are all products of this iterative approach. These advancements not only optimize the learning experience but also cater to diverse learning styles and individual needs. In essence, through continuous iterations, virtual learning platforms are striving towards a future where education can be tailored with precision while remaining accessible on a global scale.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, virtual learning offers numerous benefits such as flexibility, accessibility, and personalized learning experiences. It allows students to access a wider range of educational resources and connect with experts from around the world. However, it also comes with drawbacks including potential for distractions, lack of hands-on learning opportunities, and social isolation.
Despite its drawbacks, virtual learning has proven to be an essential tool in today’s educational landscape and has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach education. As we continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities of virtual learning, it is crucial to find a balance that maximizes its benefits while addressing its limitations.
Let’s embrace the potential of virtual learning while staying mindful of its impact on students’ overall well-being and academic success.









Pros and cons of virtual learning: Get your ultimate guide here! Learn the benefits and drawbacks of online education today!